High-resolution in vivo diffusion imaging of the human brain with generalized slice dithered enhanced resolution: Simultaneous multislice (gSlider-SMS)
- PMID: 28261904
- PMCID: PMC5585027
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26653
High-resolution in vivo diffusion imaging of the human brain with generalized slice dithered enhanced resolution: Simultaneous multislice (gSlider-SMS)
Abstract
Purpose: To develop an efficient acquisition for high-resolution diffusion imaging and allow in vivo whole-brain acquisitions at 600- to 700-μm isotropic resolution.
Methods: We combine blipped-controlled aliasing in parallel imaging simultaneous multislice (SMS) with a novel slab radiofrequency (RF) encoding gSlider (generalized slice-dithered enhanced resolution) to form a signal-to-noise ratio-efficient volumetric simultaneous multislab acquisition. Here, multiple thin slabs are acquired simultaneously with controlled aliasing, and unaliased with parallel imaging. To achieve high resolution in the slice direction, the slab is volumetrically encoded using RF encoding with a scheme similar to Hadamard encoding. However, with gSlider, the RF-encoding bases are specifically designed to be highly independent and provide high image signal-to-noise ratio in each slab acquisition to enable self-navigation of the diffusion's phase corruption. Finally, the method is combined with zoomed imaging (while retaining whole-brain coverage) to facilitate low-distortion single-shot in-plane encoding with echo-planar imaging at high resolution.
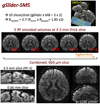
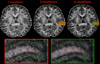
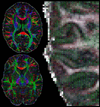
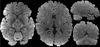
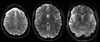
Results: A 10-slices-per-shot gSlider-SMS acquisition was used to acquire whole-brain data at 660 and 760 μm isotropic resolution with b-values of 1500 and 1800 s/mm2 , respectively. Data were acquired on the Connectome 3 Tesla scanner with 64-channel head coil. High-quality data with excellent contrast were achieved at these resolutions, which enable the visualization of fine-scale structures.
Conclusions: The gSlider-SMS approach provides a new, efficient way to acquire high-resolution diffusion data. Magn Reson Med 79:141-151, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: diffusion imaging; simultaneous multislab; simultaneous multislice; slice encoding.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Accelerated spin-echo functional MRI using multisection excitation by simultaneous spin-echo interleaving (MESSI) with complex-encoded generalized slice dithered enhanced resolution (cgSlider) simultaneous multislice echo-planar imaging.Magn Reson Med. 2020 Jul;84(1):206-220. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28108. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 31840295 Free PMC article.
-
Distortion-free, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion MRI with gSlider BUDA-EPI and multicoil dynamic B0 shimming.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Aug;86(2):791-803. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28748. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33748985 Free PMC article.
-
High-fidelity, high-isotropic-resolution diffusion imaging through gSlider acquisition with and T1 corrections and integrated ΔB0 /Rx shim array.Magn Reson Med. 2020 Jan;83(1):56-67. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27899. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 31373048 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid brain MRI acquisition techniques at ultra-high fields.NMR Biomed. 2016 Sep;29(9):1198-221. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3478. Epub 2016 Feb 2. NMR Biomed. 2016. PMID: 26835884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulse sequences and parallel imaging for high spatiotemporal resolution MRI at ultra-high field.Neuroimage. 2018 Mar;168:101-118. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28392492 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ex vivo visualization of the trigeminal pathways in the human brainstem using 11.7T diffusion MRI combined with microscopy polarized light imaging.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Jan;224(1):159-170. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1767-1. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 30293214 Free PMC article.
-
Maxwell-compensated design of asymmetric gradient waveforms for tensor-valued diffusion encoding.Magn Reson Med. 2019 Oct;82(4):1424-1437. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27828. Epub 2019 May 31. Magn Reson Med. 2019. PMID: 31148245 Free PMC article.
-
DeepDTI: High-fidelity six-direction diffusion tensor imaging using deep learning.Neuroimage. 2020 Oct 1;219:117017. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117017. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32504817 Free PMC article.
-
The State of the NIH BRAIN Initiative.J Neurosci. 2018 Jul 18;38(29):6427-6438. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3174-17.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29921715 Free PMC article.
-
Atlas-Based Adaptive Hadamard-Encoded MR Spectroscopic Imaging at 3T.Tomography. 2023 Aug 23;9(5):1592-1602. doi: 10.3390/tomography9050127. Tomography. 2023. PMID: 37736980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johansen-Berg H, Behrens TEJ, Sillery E, Ciccarelli O, Thompson AJ, Smith SM, Matthews PM. Functional-anatomical validation and individual variation of diffusion tractography-based segmentation of the human thalamus. Cereb. Cortex. 2005;15:31–39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

