Novel mechanism of metabolic co-regulation coordinates the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in Pseudomonas protegens
- PMID: 28262092
- PMCID: PMC5395296
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.22835
Novel mechanism of metabolic co-regulation coordinates the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in Pseudomonas protegens
Abstract
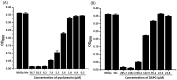
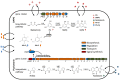
Metabolic co-regulation between biosynthetic pathways for secondary metabolites is common in microbes and can play an important role in microbial interactions. Here, we describe a novel mechanism of metabolic co-regulation in which an intermediate in one pathway is converted into signals that activate a second pathway. Our study focused on the co-regulation of 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG) and pyoluteorin, two antimicrobial metabolites produced by the soil bacterium Pseudomonas protegens. We show that an intermediate in DAPG biosynthesis, phloroglucinol, is transformed by a halogenase encoded in the pyoluteorin gene cluster into mono- and di-chlorinated phloroglucinols. The chlorinated phloroglucinols function as intra- and inter-cellular signals that induce the expression of pyoluteorin biosynthetic genes, pyoluteorin production, and pyoluteorin-mediated inhibition of the plant-pathogenic bacterium Erwinia amylovora. This metabolic co-regulation provides a strategy for P. protegens to optimize the deployment of secondary metabolites with distinct roles in cooperative and competitive microbial interactions.
Keywords: Pseudomonas protegens; biochemistry; infectious disease; metabolic co-regulation; microbiology; secondary metabolite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures












References
-
- Baehler E, Bottiglieri M, Péchy-Tarr M, Maurhofer M, Keel C. Use of green fluorescent protein-based reporters to monitor balanced production of antifungal compounds in the biocontrol agent Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 2005;99:24–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2005.02597.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bergmann S, Funk AN, Scherlach K, Schroeckh V, Shelest E, Horn U, Hertweck C, Brakhage AA. Activation of a silent fungal polyketide biosynthesis pathway through regulatory cross talk with a cryptic nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene cluster. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2010;76:8143–8149. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00683-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blackman AJ, Matthews DJ. Halogenated phloroglucinols from Rhabdonia verticillata. Phytochemistry. 1982;21:2141–2142. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(82)83072-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

