Cell-Autonomous Excitation of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons by Endocannabinoid-Dependent Lipid Signaling
- PMID: 28262417
- PMCID: PMC5672336
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.025
Cell-Autonomous Excitation of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons by Endocannabinoid-Dependent Lipid Signaling
Abstract
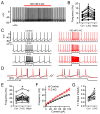
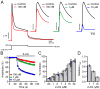
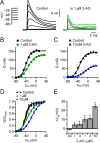
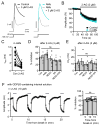
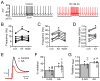
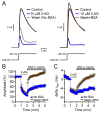
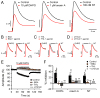
The major endocannabinoid in the mammalian brain is the bioactive lipid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). The best-known effects of 2-AG are mediated by G-protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors. In principle, 2-AG could modify neuronal excitability by acting directly on ion channels, but such mechanisms are poorly understood. Using a preparation of dissociated mouse midbrain dopamine neurons to isolate effects on intrinsic excitability, we found that 100 nM 2-AG accelerated pacemaking and steepened the frequency-current relationship for burst-like firing. In voltage-clamp experiments, 2-AG reduced A-type potassium current (IA) through a cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanism mimicked by arachidonic acid, which has no activity on cannabinoid receptors. Activation of orexin, neurotensin, and metabotropic glutamate Gq/11-linked receptors mimicked the effects of exogenous 2-AG and their actions were prevented by inhibiting the 2-AG-synthesizing enzyme diacylglycerol lipase α. The results show that 2-AG and related lipid signaling molecules can directly tune neuronal excitability in a cell-autonomous manner by modulating IA.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Synaptic transmission: Changing the (potassium) channel?Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 May;18(5):266. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.41. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28331233 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Suppresses LPS-Induced Inhibition of A-Type Potassium Channel Currents in Caudate Nucleus Neurons Through CB1 Receptor.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Aug;59(4):493-503. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0761-4. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27129498
-
Neurotensin inhibits glutamate-mediated synaptic inputs onto ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons through the release of the endocannabinoid 2-AG.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Nov;63(6):983-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.07.037. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22884466
-
Targeting the cannabinoid system for pain relief?Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2013 Dec;51(4):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.aat.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2013. PMID: 24529672 Review.
-
Endocannabinoid-mediated modulation of Gq/11 protein-coupled receptor signaling-induced vasoconstriction and hypertension.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Mar 5;403:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.01.012. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25595485
-
No more pain upon Gq-protein-coupled receptor activation: role of endocannabinoids.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Feb;39(3):467-84. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12475. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. Retraction in: Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Apr;43(7):991. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13231. PMID: 24494686 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Muscarinic receptor activation preferentially inhibits rebound in vulnerable dopaminergic neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 31:2024.07.30.605819. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.30.605819. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Apr 16;45(16):e1443242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1443-24.2025. PMID: 39131326 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Interplay between endocannabinoids and dopamine in the basal ganglia: implications for pain in Parkinson's disease.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 May 14;4(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00169-z. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 38745258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic transmission: Changing the (potassium) channel?Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 May;18(5):266. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.41. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28331233 No abstract available.
-
Cannabinoids in the descending pain modulatory circuit: Role in inflammation.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 May;209:107495. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107495. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32004514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabinoids Stimulate the TRP Channel-Dependent Release of Both Serotonin and Dopamine to Modulate Behavior in C. elegans.J Neurosci. 2019 May 22;39(21):4142-4152. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2371-18.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 18. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30886012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amorós I, Barana A, Caballero R, Gómez R, Osuna L, Lillo MP, Tamargo J, Delpón E. Endocannabinoids and cannabinoid analogues block human cardiac Kv4.3 channels in a receptor-independent manner. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2010;48:201–210. - PubMed
-
- Bacci A, Huguenard JR, Prince DA. Long-lasting self-inhibition of neocortical interneurons mediated by endocannabinoids. Nature. 2004;431:312–316. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

