Laser irradiated fluorescent perfluorocarbon microparticles in 2-D and 3-D breast cancer cell models
- PMID: 28262671
- PMCID: PMC5338257
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43408
Laser irradiated fluorescent perfluorocarbon microparticles in 2-D and 3-D breast cancer cell models
Abstract
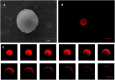
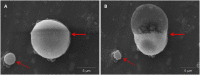
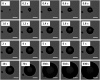
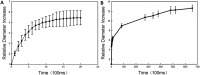
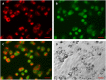
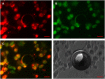
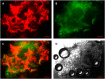
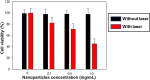
Perfluorocarbon (PFC) droplets were studied as new generation ultrasound contrast agents via acoustic or optical droplet vaporization (ADV or ODV). Little is known about the ODV irradiated vaporization mechanisms of PFC-microparticle complexs and the stability of the new bubbles produced. In this study, fluorescent perfluorohexane (PFH) poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) particles were used as a model to study the process of particle vaporization and bubble stability following excitation in two-dimensional (2-D) and three-dimensional (3-D) cell models. We observed localization of the fluorescent agent on the microparticle coating material initially and after vaporization under fluorescence microscopy. Furthermore, the stability and growth dynamics of the newly created bubbles were observed for 11 min following vaporization. The particles were co-cultured with 2-D cells to form 3-D spheroids and could be vaporized even when encapsulated within the spheroids via laser irradiation, which provides an effective basis for further work.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Rapoport N., Gao Z. & Kennedy A. Multifunctional nanoparticles for combining ultrasonic tumor imaging and targeted chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 99, 1095–1106 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Huang J., Xu J. S. & Xu R. X. Heat-sensitive microbubbles for intraoperative assessment of cancer ablation margins. Biomaterials 31, 1278–1286 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y. et al. Phase-Shifted PFH@PLGA/Fe3O4 Nanocapsules for MRI/US Imaging and Photothermal Therapy with near-Infrared Irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7, 14231–14242 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

