Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog expression correlates with clinicopathological features of non-small cell lung cancer patients and its impact on survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28263037
- PMCID: PMC5415467
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12425
Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog expression correlates with clinicopathological features of non-small cell lung cancer patients and its impact on survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Phosphatase and tensin homolog ( PTEN ), regarded as a tumor suppressor gene, may act as a prognostic biomarker in human cancers.
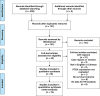
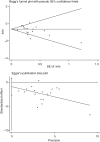
Methods: All eligible studies from MEDLINE, Embase, CENTRAL, and the Chinese BioMedical Literature Database to October 2016 were incorporated. Two reviewers independently screened the literature according to inclusion and exclusion criteria, extracted the data, assessed the methodological quality of the included studies, and conducted meta-analysis.
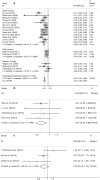
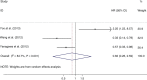
Results: A total of 2486 patients from 19 studies were included. PTEN expression was significantly correlated with gender, smoking history, histology (adenocarcinoma [ADC] vs. squamous cell carcinoma), tumor node metastasis stage (I-II vs. III-IV), N status (N0 vs. N1-N3), and distant metastasis (M0 vs. M1). Loss of PTEN expression was associated with poorer overall survival, but had no significant association with disease-free survival. Subgroup analysis showed that negative PTEN expression was associated with a poorer outcome in Asian and ADC patients, but not in Western or squamous cell carcinoma patients.
Conclusion: Loss of PTEN might play an unfavorable prognostic role for overall survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients, especially Asian or ADC patients.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; non-small cell lung cancer; phosphatase and tensin homolog; prognosis.
© 2017 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog and programmed cell death ligand 1 in adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 18;503(4):2764-2769. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.037. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30100056
-
Loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog protein expression is an independent poor prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Oct;7(10):1513-21. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182641d4f. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22982652
-
High levels of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Expression Predict Favorable Prognosis in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015 Dec;73(3):631-7. doi: 10.1007/s12013-015-0671-z. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 27259304
-
Clinicopathological significance and potential drug target of RUNX3 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jun 3;9:2855-65. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S76358. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26082616 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog) in gastric cancer development and progression.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(1):17-24. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.1.17. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24528021 Review.
Cited by
-
Precise Immunodetection of PTEN Protein in Human Neoplasia.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019 Dec 2;9(12):a036293. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a036293. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019. PMID: 31501265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Candidate Biomarkers Correlated With the Pathogenesis and Prognosis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Genet. 2018 Oct 12;9:469. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00469. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30369945 Free PMC article.
-
FAM46B suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer via β-catenin/MMP7 signaling.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Aug;8(4):1497-1505. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.27. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35116892 Free PMC article.
-
The Smad4/PTEN Expression Pattern Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma.J Pathol Transl Med. 2018 Jan;52(1):37-44. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2017.10.20. Epub 2017 Oct 23. J Pathol Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29056035 Free PMC article.
-
Pectolinarigenin inhibits non‑small cell lung cancer progression by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Dec;40(6):3458-3468. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6759. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30542737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. (Published erratum appears in CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 134.) CA Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90. - PubMed
-
- Bunn PA Jr. Worldwide overview of the current status of lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012; 136: 1478–81. - PubMed
-
- Zhang T, Zhang DM, Zhao D et al. The prognostic value of osteopontin expression in non‐small cell lung cancer: A meta‐analysis. J Mol Histol 2014; 45: 533–40. - PubMed
-
- Liang Y, Guo S, Zhou Q. Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase‐7 expression in patients with non‐small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: 3717–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

