The accumulation of lipids and proteins during red blood cell storage: the roles of leucoreduction and experimental filtration
- PMID: 28263170
- PMCID: PMC5336334
- DOI: 10.2450/2017.0314-16
The accumulation of lipids and proteins during red blood cell storage: the roles of leucoreduction and experimental filtration
Abstract
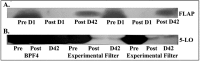
Pre-storage leucoreduction has been universally adopted in most developed countries in Asia, Europe and the Americas. It decreases febrile transfusion reactions, alloimmunisation to HLA antigens, cytomegalovirus exposure, the accumulation of a number of pro-inflammatory mediators in the supernatant, including the accumulation of platelet-and leucocyte-derived proteins and metabolites during routine storage. This review will highlight the lipids and proteins, biological response modifiers (BRMs) that accumulate, their clinical effects in transfused hosts, and methods of mitigation.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hebert PC, Fergusson D, Blajchman MA, et al. Clinical outcomes following institution of the Canadian universal leukoreduction program for red blood cell transfusions. JAMA. 2003;289:1941–9. - PubMed
-
- McFaul SJ, Corley JB, Mester CW, Nath J. Packed blood cells stored in AS-5 become proinflammatory during storage. Transfusion. 2009;49:1451–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
