Whole genome sequencing resource identifies 18 new candidate genes for autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 28263302
- PMCID: PMC5501701
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4524
Whole genome sequencing resource identifies 18 new candidate genes for autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
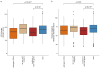
We are performing whole-genome sequencing of families with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to build a resource (MSSNG) for subcategorizing the phenotypes and underlying genetic factors involved. Here we report sequencing of 5,205 samples from families with ASD, accompanied by clinical information, creating a database accessible on a cloud platform and through a controlled-access internet portal. We found an average of 73.8 de novo single nucleotide variants and 12.6 de novo insertions and deletions or copy number variations per ASD subject. We identified 18 new candidate ASD-risk genes and found that participants bearing mutations in susceptibility genes had significantly lower adaptive ability (P = 6 × 10-4). In 294 of 2,620 (11.2%) of ASD cases, a molecular basis could be determined and 7.2% of these carried copy number variations and/or chromosomal abnormalities, emphasizing the importance of detecting all forms of genetic variation as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in ASD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Lai MC, Lombardo MV, Baron-Cohen S. Autism. Lancet. 2014;383:896–910. - PubMed
-
- Carter MT, Scherer SW. Autism spectrum disorder in the genetics clinic: a review. Clin Genet. 2013;83:399–407. - PubMed
-
- Miles JH. Complex Autism Spectrum Disorders and Cutting-Edge Molecular Diagnostic Tests. JAMA. 2015;314:879–880. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

