A Bayesian Target Predictor Method based on Molecular Pairing Energies estimation
- PMID: 28263323
- PMCID: PMC5338323
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43738
A Bayesian Target Predictor Method based on Molecular Pairing Energies estimation
Abstract
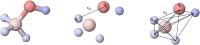
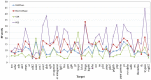
Virtual screening (VS) is applied in the early drug discovery phases for the quick inspection of huge molecular databases to identify those compounds that most likely bind to a given drug target. In this context, there is the necessity of the use of compact molecular models for database screening and precise target prediction in reasonable times. In this work we present a new compact energy-based model that is tested for its application to Virtual Screening and target prediction. The model can be used to quickly identify active compounds in huge databases based on the estimation of the molecule's pairing energies. The greatest molecular polar regions along with its geometrical distribution are considered by using a short set of smart energy vectors. The model is tested using similarity searches within the Directory of Useful Decoys (DUD) database. The results obtained are considerably better than previously published models. As a Target prediction methodology we propose the use of a Bayesian Classifier that uses a combination of different active compounds to build an energy-dependent probability distribution function for each target.
Conflict of interest statement
The proposed molecular descriptors are protected under the patent number ES 2551250 B1.
Figures



References
-
- Rester U. From virtuality to reality - Virtual screening in lead discovery and lead optimization: a medicinal chemistry perspective. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 11, 559–568 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Warren G. L. et al.. A critical assessment of docking programs and scoring functions. J. Med. Chem. 49, 5912–5931 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Wong S. E. & Lightstone F. C. Message passing interface and multithreading hybrid for parallel molecular docking of large databases on petascale high performance computing machines. J. Comput. Chem. 34, 915–927 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Hristozov D. P., Oprea T. I. & Gasteiger J. Virtual screening applications: A study of ligand-based methods and different structure representations in four different scenarios. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 21, 617–640 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ling X., Jeffrey W. G. & Jürgen B. Database Searching for Compounds with Similar Biological Activity Using Short Binary Bit String Representations of Molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 39, 881–886 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

