Genome-wide mapping of long-range contacts unveils clustering of DNA double-strand breaks at damaged active genes
- PMID: 28263325
- PMCID: PMC5385132
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3387
Genome-wide mapping of long-range contacts unveils clustering of DNA double-strand breaks at damaged active genes
Abstract
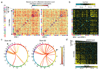
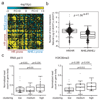
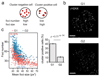
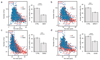
The ability of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) to cluster in mammalian cells has been a subject of intense debate in recent years. Here we used a high-throughput chromosome conformation capture assay (capture Hi-C) to investigate clustering of DSBs induced at defined loci in the human genome. The results unambiguously demonstrated that DSBs cluster, but only when they are induced within transcriptionally active genes. Clustering of damaged genes occurs primarily during the G1 cell-cycle phase and coincides with delayed repair. Moreover, DSB clustering depends on the MRN complex as well as the Formin 2 (FMN2) nuclear actin organizer and the linker of nuclear and cytoplasmic skeleton (LINC) complex, thus suggesting that active mechanisms promote clustering. This work reveals that, when damaged, active genes, compared with the rest of the genome, exhibit a distinctive behavior, remaining largely unrepaired and clustered in G1, and being repaired via homologous recombination in postreplicative cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

