A Chemical Probe Strategy for Interrogating Inhibitor Selectivity Across the MEK Kinase Family
- PMID: 28263556
- PMCID: PMC5652073
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b01060
A Chemical Probe Strategy for Interrogating Inhibitor Selectivity Across the MEK Kinase Family
Abstract
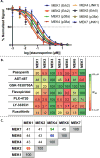
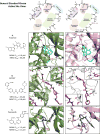
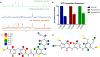
MEK4 is an upstream kinase in MAPK signaling pathways where it phosphorylates p38 MAPK and JNK in response to mitogenic and cellular stress queues. MEK4 is overexpressed and induces metastasis in advanced prostate cancer lesions. However, the value of MEK4 as an oncology target has not been pharmacologically validated because selective chemical probes targeting MEK4 have not been developed. Despite a high level of sequence homology in the ATP-binding site, most reported MEK inhibitors are selective for MEK1/2 and display reduced potency toward other MEKs. Here, we present the first functional and binding selectivity-profiling platform of the MEK family. We applied the platform to profile a set of known kinase inhibitors and used the results to develop an in silico approach for small molecule docking against MEK proteins. The docking studies identified molecular features of the ligands and corresponding amino acids in MEK proteins responsible for high affinity binding versus those driving selectivity. WaterLOGSY and saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR spectroscopy techniques were utilized to understand the binding modes of active compounds. Further minor synthetic manipulations provide a proof of concept by showing how information gained through this platform can be utilized to perturb selectivity across the MEK family. This inhibitor-based approach pinpoints key features governing MEK family selectivity and clarifies empirical selectivity profiles for a set of kinase inhibitors. Going forward, the platform provides a rationale for facilitating the development of MEK-selective inhibitors, particularly MEK4 selective inhibitors, and repurposing of kinase inhibitors for probing the structural selectivity of isoforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

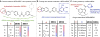
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 3-Arylindazoles as Selective MEK4 Inhibitors.ChemMedChem. 2019 Mar 22;14(6):615-620. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900019. Epub 2019 Feb 19. ChemMedChem. 2019. PMID: 30707493 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling MEK4 Kinase Inhibitors through Perturbed Electrostatic Potential Charges.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Oct 28;59(10):4460-4466. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00490. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 31566378 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the unfolded protein response stress sensor ERN1 in regulating the response to MEK inhibitors in KRAS mutant colon cancers.Genome Med. 2018 Nov 27;10(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13073-018-0600-z. Genome Med. 2018. PMID: 30482246 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1/2 inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic malignancies.Gynecol Oncol. 2014 Apr;133(1):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Gynecol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24434059 Review.
-
Recent developments in mitogen activated protein kinase inhibitors as potential anticancer agents.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Sep;114:105161. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105161. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34328852 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-'classical' MEKs: A review of MEK3-7 inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jul 1;30(13):127203. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127203. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32389527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Design of Highly Potent and Selective Covalent MAP2K7 Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Apr 17;14(5):606-613. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00029. eCollection 2023 May 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37197477 Free PMC article.
-
Pazopanib alleviates neuroinflammation and protects dopaminergic neurons in LPS-stimulated mouse model by inhibiting MEK4-JNK-AP-1 pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Jun;44(6):1135-1148. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-01030-1. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36536076 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design, Optimization, and Biological Evaluation of Novel MEK4 Inhibitors against Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021 Sep 15;12(10):1559-1567. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00376. eCollection 2021 Oct 14. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34676038 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the MAP2K7-JNK pathway with 5Z-7-oxozeaenol induces apoptosis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Oncotarget. 2021 Aug 31;12(18):1787-1801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28040. eCollection 2021 Aug 31. Oncotarget. 2021. PMID: 34504651 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

