Encapsulation, controlled release, and antitumor efficacy of cisplatin delivered in liposomes composed of sterol-modified phospholipids
- PMID: 28263913
- PMCID: PMC5473525
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.03.003
Encapsulation, controlled release, and antitumor efficacy of cisplatin delivered in liposomes composed of sterol-modified phospholipids
Abstract
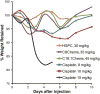
We employed a recently introduced class of sterol-modified lipids (SML) to produce m-PEG-DSPE containing liposome compositions with a range of cis-platinum content release rates. SML have a cholesterol succinate attached to the phosphatidylglycerol head group and a fatty acid at the 2 position. These compositions were compared to the well-studied liposome phospholipid compositions: mPEG-DSPE/Hydrogenated Soy PC/cholesterol or mPEG-DSPE/POPC/cholesterol to determine the effect of the cis-platinum release extent on C26 tumor proliferation in the BALB/c colon carcinoma mouse model. The release rates of cis-platinum from liposomes composed of SML are a function of the acyl chain length. SML-liposomes with shorter acyl chain lengths C-8 provided more rapid cisplatin release, lower in vitro IC50, and were easier to formulate compared to liposomes using traditional phospholipid compositions. Similar to other liposome cis-platinum formulations, the half-life of m-PEG-DSPE SML liposome cisplatin is substantially longer than the free drug. This resulted in a higher tumor cisplatin concentration at 48h post-dosing compared to the free drug and higher Pt-DNA adducts in the tumor. Moreover, the maximum tolerated dose of the liposome formulations where up to four fold greater than the free drug. Using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy on tumor sections, we compared the location of platinum, to the location of a fluorescence lipid incorporated in the liposomes. The liposome platinum co-localized with the fluorescent lipid and both were non-uniformly distributed in the tumor. Non-encapsulated Cis-platinum, albeit at a low concentration, was more uniformly distributed thorough the tumor. Three liposome formulations, including the well-studied hydrogenated HSPC composition, had better antitumor activity in the murine colon 26 carcinoma model as compared to the free drug at the same dose but the SML liposome platinum formulations did not perform better than the HSPC formulation.
Keywords: C26 colon carcinoma; Cisplatin; Liposome; Sterol-modified phospholipid; X-ray fluorescence microscopy.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


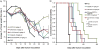

Similar articles
-
The influence of phospholipid on the physicochemical properties and anti-tumor efficacy of liposomes encapsulating cisplatin in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma.Int J Pharm. 2014 Oct 1;473(1-2):326-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.07.020. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Int J Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25051111
-
Comparative pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and therapeutic effectiveness of cisplatin encapsulated in long-circulating, pegylated liposomes (SPI-077) in tumor-bearing mice.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(1):1-7. doi: 10.1007/s002800050855. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 9923534
-
Optimizing the therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin PEGylated liposomes via incorporation of different DPPG ratios: In vitro and in vivo studies.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015 Dec 1;136:885-91. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.10.046. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015. PMID: 26547316
-
Pharmacology of drugs formulated with DepoFoam: a sustained release drug delivery system for parenteral administration using multivesicular liposome technology.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45(12):1153-76. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200645120-00002. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006. PMID: 17112293 Review.
-
The latest advances of cisplatin liposomal formulations: essentials for preparation and analysis.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Apr;17(4):523-541. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1737672. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32116060 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoencapsulation of Hirudo medicinalis proteins in liposomes as a nanocarrier for inhibiting angiogenesis through targeting VEGFA in the Breast cancer cell line (MCF-7).Bioimpacts. 2022;12(2):115-126. doi: 10.34172/bi.2021.39. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Bioimpacts. 2022. PMID: 35411300 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Encapsulation of Fisetin and Cisplatin into Liposomes for Glioma Therapy: From Formulation to Cell Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):970. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070970. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34206986 Free PMC article.
-
Collagenase Nanoparticles Enhance the Penetration of Drugs into Pancreatic Tumors.ACS Nano. 2019 Oct 22;13(10):11008-11021. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b02395. Epub 2019 Sep 20. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 31503443 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Efficacy of PEGylated Liposomal Cisplatin: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 15;21(2):559. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020559. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31952316 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells As Guideposts for Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeted Drug Delivery in Ovarian Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 14;12(4):965. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040965. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32295145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alavizadeh SH, Badiee A, Golmohammadzadeh S, Jaafari MR. The influence of phospholipid on the physicochemical properties and anti-tumor efficacy of liposomes encapsulating cisplatin in mice bearing C26 colon carcinoma. Int J Pharm. 2014;473:326–333. - PubMed
-
- Bandak S, Goren D, Horowitz A, Tzemach D, Gabizon A. Pharmacological studies of cisplatin encapsulated in long-circulating liposomes in mouse tumor models. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 1999;10:911–920. - PubMed
-
- Dos Santos N, Mayer LD, Abraham SA, Gallagher RC, Cox KAK, Tardi PG, Bally MB. Improved retention of idarubicin after intravenous injection obtained for cholesterol-free liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2002;1561:188–201. - PubMed
-
- Dou YN, Dunne M, Huang H, Mckee T, Chang MC, Jaffray DS, Allen C. Thermosensitive liposomal cisplatin in combination with local hyperthermia results in tumor growth delay and changes in tumor microenvironment in xenograft models of lung carcinoma. J Drug Target. 2016;24:865–877. - PubMed
-
- Dragovich T, Mendelson D, Kurtin S, Richardson K, Von Hoff D, Hoos A. A Phase 2 trial of the liposomal DACH platinum L-NDDP in patients with therapy-refractory advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006;58:759–764. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

