Power analysis of single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments
- PMID: 28263961
- PMCID: PMC5376499
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4220
Power analysis of single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments
Abstract
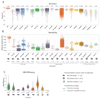
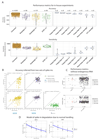
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has become an established and powerful method to investigate transcriptomic cell-to-cell variation, thereby revealing new cell types and providing insights into developmental processes and transcriptional stochasticity. A key question is how the variety of available protocols compare in terms of their ability to detect and accurately quantify gene expression. Here, we assessed the protocol sensitivity and accuracy of many published data sets, on the basis of spike-in standards and uniform data processing. For our workflow, we developed a flexible tool for counting the number of unique molecular identifiers (https://github.com/vals/umis/). We compared 15 protocols computationally and 4 protocols experimentally for batch-matched cell populations, in addition to investigating the effects of spike-in molecular degradation. Our analysis provides an integrated framework for comparing scRNA-seq protocols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Stegle O, Teichmann SA, Marioni JC. Computational and analytical challenges in single-cell transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16:133–145. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

