Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD
- PMID: 28264439
- PMCID: PMC5372871
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9030208
Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD
Abstract
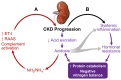
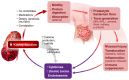
Elevated protein catabolism and protein malnutrition are common in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The underlying etiology includes, but is not limited to, metabolic acidosis intestinal dysbiosis; systemic inflammation with activation of complements, endothelin-1 and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS) axis; anabolic hormone resistance; energy expenditure elevation; and uremic toxin accumulation. All of these derangements can further worsen kidney function, leading to poor patient outcomes. Many of these CKD-related derangements can be prevented and substantially reversed, representing an area of great potential to improve CKD and ESRD care. This review integrates known information and recent advances in the area of protein nutrition and malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Management recommendations are summarized. Thorough understanding the pathogenesis and etiology of protein malnutrition in CKD and ESRD patients will undoubtedly facilitate the design and development of more effective strategies to optimize protein nutrition and improve outcomes.
Keywords: protein nutrition; acidosis; chronic kidney disease; dialysis; inflammation; protein catabolism; hormonal derangements; uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- 2015 USRDS Annual Data Report. Volume 2. [(accessed on 14 January 2017)]. Available online: https://www.usrds.org/2015/download/vol2_USRDS_ESRD_15.pdf.
-
- Ikizler T.A., Cano N.J., Franch H., Fouque D., Himmelfarb J., Kalantar-Zadeh K., Kuhlmann M.K., Stenvinkel P., TerWee P., Teta D., et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013;84:1096–1107. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gracia-Iguacel C., González-Parra E., Pérez-Gómez M.V., Mahíllo I., Egido J., Ortiz A., Carrero J.J. Prevalence of protein-energy wasting syndrome and its association with mortality in haemodialysis patients in a centre in Spain. Nefrologia. 2013;33:495–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

