Paeoniflorin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Injury by Regulating Ca2+/CaMKII/CREB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 28264448
- PMCID: PMC6155252
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22030359
Paeoniflorin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Injury by Regulating Ca2+/CaMKII/CREB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
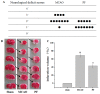
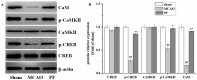
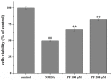
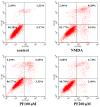
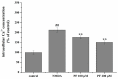
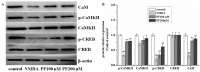
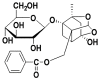
Paeoniflorin (PF) is an active ingredient of Paeoniae Radix which possesses the neuroprotective effect. However, so far, the neuroprotective mechanism of PF has still not been fully uncovered. The Ca2+/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)/cAMP response element-binding (CREB) signaling pathway plays an important role in the intracellular signal transduction pathway involved in cell proliferation, cell survival, inflammation and metabolism. Herein, the neuroprotective roles of PF in the models of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) followed by reperfusion in rats and N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA)-induced excitotoxicity in primary hippocampal neurons were investigated. Moreover, we attempted to confirm the hypothesis that its protection effect is via the modulation of the Ca2+/CaMKI)/CREB signaling pathway. In this study, PF not only significantly decreased neurological deficit scores and infarct volume in vivo, but also improved neurons' cell viability, and inhibited neurons' apoptosis and intracellular Ca2+ concentration in vitro. Furthermore, PF significantly up-regulated p-CREB and p-CaMKII, and down-regulated calmodulin (CaM) in vivo and in vitro. The results indicate that the protective effect of PF on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury is possible through regulating the Ca2+/CaMKII/CREB signaling pathway.
Keywords: CREB; CaMKII; ischemic stroke; middle cerebral artery occlusion; paeoniflorin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Go A.S., Mozaffarian D., Roger V.L., Benjamin E.J., Berry J.D., Blaha M.J., Dai S., Ford E.S., Fox C.S., Franco S., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–e292. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000441139.02102.80. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lees K.R., Bluhmki E., von Kummer R., Brott T.G., Toni D., Grotta J.C., Albers G.W., Kaste M., Marler J.R., Hamilton S.A., et al. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: An updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHE Ttrials. Lancet. 2010;375:1695–1703. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60491-6. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

