Ovalbumin with Glycated Carboxyl Groups Shows Membrane-Damaging Activity
- PMID: 28264493
- PMCID: PMC5372536
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18030520
Ovalbumin with Glycated Carboxyl Groups Shows Membrane-Damaging Activity
Abstract
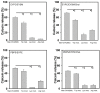
The aim of the present study was to investigate whether glycated ovalbumin (OVA) showed novel activity at the lipid-water interface. Mannosylated OVA (Man-OVA) was prepared by modification of the carboxyl groups with p-aminophenyl α-dextro (d)-mannopyranoside. An increase in the number of modified carboxyl groups increased the membrane-damaging activity of Man-OVA on cell membrane-mimicking vesicles, whereas OVA did not induce membrane permeability in the tested phospholipid vesicles. The glycation of carboxyl groups caused a notable change in the gross conformation of OVA. Moreover, owing to their spatial positions, the Trp residues in Man-OVA were more exposed, unlike those in OVA. Fluorescence quenching studies suggested that the Trp residues in Man-OVA were located on the interface binds with the lipid vesicles, and their microenvironment was abundant in positively charged residues. Although OVA and Man-OVA showed a similar binding affinity for lipid vesicles, the lipid-interacting feature of Man-OVA was distinct from that of OVA. Chemical modification studies revealed that Lys and Arg residues, but not Trp residues, played a crucial role in the membrane-damaging activity of Man-OVA. Taken together, our data suggest that glycation of carboxyl groups causes changes in the structural properties and membrane-interacting features of OVA, generating OVA with membrane-perturbing activities at the lipid-water interface.
Keywords: carboxyl group; glycation; membrane-damaging activity; ovalbumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Membrane-damaging activities of mannosylated ovalbumin are involved in its antibacterial action.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018 Feb 1;639:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.12.006. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2018. PMID: 29273433
-
Bovine serum albumin with glycated carboxyl groups shows membrane-perturbing activities.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Dec 15;564:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25449061
-
Differential binding to phospholipid bilayers modulates membrane-damaging activity of Naja naja atra cardiotoxins.Toxicon. 2009 Sep 1;54(3):321-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.04.024. Epub 2009 May 18. Toxicon. 2009. PMID: 19450618
-
Mechanisms of isoquercitrin attenuates ovalbumin glycation: Investigation by spectroscopy, spectrometry and molecular docking.Food Chem. 2020 Mar 30;309:125667. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125667. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 31679851
-
Molecular parameters involved in aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity.J Toxicol Environ Health. 1995 Mar;44(3):263-300. doi: 10.1080/15287399509531960. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1995. PMID: 7897692 Review.
Cited by
-
DMTMM-Mediated Intramolecular Cyclization of Acidic Residues in Peptides/Proteins.ACS Omega. 2021 Feb 5;6(7):4708-4718. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05503. eCollection 2021 Feb 23. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33644578 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxyl Group-Modified Myoglobin Induces TNF-α-Mediated Apoptosis in Leukemia Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 27;15(9):1066. doi: 10.3390/ph15091066. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palomo J.M., Fernandez-Lorente G., Guisan J.M., Fernandez-Lafuente R. Modulation of immobilized lipase enatioselectivity via chemical amination. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007;349:1119–1127. doi: 10.1002/adsc.200600555. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

