Hearing Improvement in A/J Mice via the Mouse Nerve Growth Factor
- PMID: 28264554
- PMCID: PMC5678043
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2016.01354
Hearing Improvement in A/J Mice via the Mouse Nerve Growth Factor
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the otoprotective effects of mouse nerve growth factor (mNGF) in A/J mice.
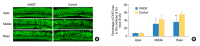
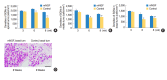
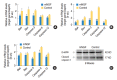
Methods: The mice at postnatal day 7 (P7) were randomly separated into a mNGF treated group (mNGF group) and a distilled water (for injection) treated group (control group). The mNGF dissolved in distilled water or distilled water alone was given to the mice once every other day from P7 by intramuscular injection in the hips. The otoprotective effects of mNGF in A/J mice were observed in a time course manner. The thresholds of auditory-evoked brainstem response (ABR) were tested from the age of the 3rd to the 8th week. Sections of the inner ears were stained by hematoxylin and eosin, and spiral ganglion neurons (SGNs) were observed at the age of the 3rd, the 6th,and the 8th week. Counts of whole mount outer hair cells (OHCs) in the cochleae were made at the age of 8 weeks. Expression of apoptosis related genes was determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Results: ABR thresholds of the mNGF group were significantly lower than those of the control group at the age of the 6th and the 8th week. Moreover, the mNGF preserved OHC and SGN in the mouse cochleae in this period. Further experiments showed that the expression of caspase genes (including caspase-3) was inhibited in the mouse inner ears in the mNGF group.
Conclusion: The mNGF improves hearing in A/J mice by preserving SGN and OHC in the cochleae.
Keywords: Hair Cells; Nerve Growth Factor; Neurons; Protection.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson KR, Erway LC, Cook SA, Willott JF, Zheng QY. A major gene affecting age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6J mice. Hear Res. 1997 Dec;114(1-2):83–92. - PubMed
-
- Johnson KR, Zheng QY, Erway LC. A major gene affecting age-related hearing loss is common to at least ten inbred strains of mice. Genomics. 2000 Dec;70(2):171–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

