Overcoming an Extremely Drug Resistant (XDR) Pathogen: Avibactam Restores Susceptibility to Ceftazidime for Burkholderia cepacia Complex Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients
- PMID: 28264560
- PMCID: PMC5560099
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.7b00020
Overcoming an Extremely Drug Resistant (XDR) Pathogen: Avibactam Restores Susceptibility to Ceftazidime for Burkholderia cepacia Complex Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients
Abstract
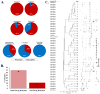
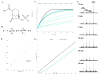
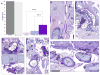
Burkholderia multivorans is a significant health threat to persons with cystic fibrosis (CF). Infections are difficult to treat as this pathogen is inherently resistant to multiple antibiotics. Susceptibility testing of isolates obtained from CF respiratory cultures revealed that single agents selected from different antibiotic classes were unable to inhibit growth. However, all isolates were found to be susceptible to ceftazidime when combined with the novel non-β-lactam β-lactamase inhibitor, avibactam (all minimum inhibitor concentrations (MICs) were ≤8 mg/L of ceftazidime and 4 mg/L of avibactam). Furthermore, a major β-lactam resistance determinant expressed in B. multivorans, the class A carbapenemase, PenA was readily inhibited by avibactam with a high k2/K of (2 ± 1) × 106 μM-1 s-1 and a slow koff of (2 ± 1) × 10-3 s-1. Mass spectrometry revealed that avibactam formed a stable complex with PenA for up to 24 h and that avibactam recyclized off of PenA, re-forming the active compound. Crystallographic analysis of PenA-avibactam revealed several interactions that stabilized the acyl-enzyme complex. The deacylation water molecule possessed decreased nucleophilicity, preventing decarbamylation. In addition, the hydrogen-bonding interactions with Lys-73 were suggestive of a protonated state. Thus, Lys-73 was unlikely to abstract a proton from Ser-130 to initiate recyclization. Using Galleria mellonella larvae as a model for infection, ceftazidime-avibactam was shown to significantly (p < 0.001) improve survival of larvae infected with B. multivorans. To further support the translational impact, the ceftazidime-avibactam combination was evaluated using susceptibility testing against other strains of Burkholderia spp. that commonly infect individuals with CF, and 90% of the isolates were susceptible to the combination. In summary, ceftazidime-avibactam may serve as a preferred therapy for people that have CF and develop Burkholderia spp. infections and should be considered for clinical trials.
Keywords: Burkholderia; avibactam; ceftazidime; cystic fibrosis; β-lactamase; β-lactamase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
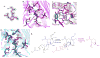
Similar articles
-
Activity of Imipenem-Relebactam against Multidrug- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Burkholderia cepacia Complex and Burkholderia gladioli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Oct 18;65(11):e0133221. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01332-21. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34370574 Free PMC article.
-
"Switching Partners": Piperacillin-Avibactam Is a Highly Potent Combination against Multidrug-Resistant Burkholderia cepacia Complex and Burkholderia gladioli Cystic Fibrosis Isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Jul 26;57(8):e00181-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00181-19. Print 2019 Aug. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31167848 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of the Ω-Loop in the Evolution of Ceftazidime Resistance in the PenA β-Lactamase from Burkholderia multivorans, an Important Cystic Fibrosis Pathogen.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01941-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01941-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27872073 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on ceftazidime-avibactam for optimizing outcomes in complicated intra-abdominal and urinary tract infections.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(9):1261-73. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2015.1062873. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26145447 Review.
-
[An opportunistic pathogen frequently isolated from immunocompromised patients: Burkholderia cepacia complex].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012 Apr;46(2):304-18. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2012. PMID: 22639321 Review. Turkish.
Cited by
-
Activity of ETX0462 toward Some Burkholderia spp.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Jan 24;67(1):e0135222. doi: 10.1128/aac.01352-22. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36507667 Free PMC article.
-
Lung transplantation in two cystic fibrosis patients infected with previously pandrug-resistant Burkholderia cepacia complex treated with ceftazidime-avibactam.Infection. 2019 Apr;47(2):289-292. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-1261-y. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Infection. 2019. PMID: 30565008
-
Ceftazidime/Avibactam in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Due to Difficult-to-Treat Non-Fermenter Gram-Negative Bacteria in COVID-19 Patients: A Case Series and Review of the Literature.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1007. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081007. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892396 Free PMC article.
-
Resurrecting Old β-Lactams: Potent Inhibitory Activity of Temocillin against Multidrug-Resistant Burkholderia Species Isolates from the United States.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Mar 27;63(4):e02315-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02315-18. Print 2019 Apr. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 30718248 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of Imipenem-Relebactam against Multidrug- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Burkholderia cepacia Complex and Burkholderia gladioli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Oct 18;65(11):e0133221. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01332-21. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34370574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. https://www.cff.org/
- Elborn JS. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 2016;388(10059):2519–2531. - PubMed
-
- Horsley A, Jones AM, Lord R. Antibiotic treatment for Burkholderia cepacia complex in people with cystic fibrosis experiencing a pulmonary exacerbation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev No. 2016;1:CD009529. - PMC - PubMed
- Regan KH, Bhatt J. Eradication therapy for Burkholderia cepacia complex in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;11:CD009876. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

