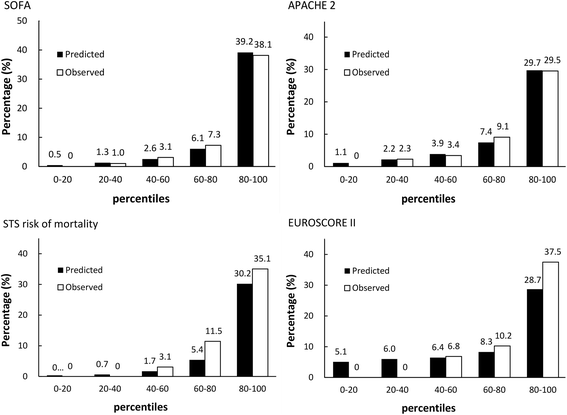
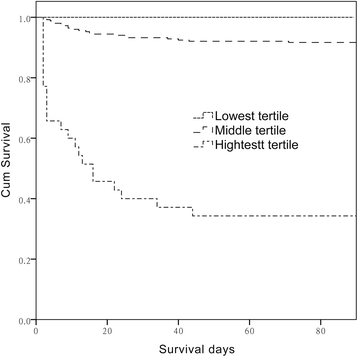
Sequential organ failure assessment score predicts mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting
- PMID: 28264675
- PMCID: PMC5339985
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-017-0219-9
Sequential organ failure assessment score predicts mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting
Abstract
Background: Mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is generally associated with underlying disease and surgical factors overlooked in preoperative prognostic models. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE II) scores are widely used in intensive care units for outcome prediction. This study investigated the accuracy of these models in predicting mortality.
Methods: Between January 2010 and April 2013, 483 patients who underwent isolated CABG were enrolled. The clinical characteristics, outcomes, and prognostic model scores of the patients were collected. Discrimination was assessed using the area under the curve approach.
Results: Both SOFA and APACHE II scores were effective for predicting in-hospital mortality. Among the organ systems examined in the SOFA, the cardiac and renal systems were the strongest predictors of CABG mortality. Multivariate analysis identified only the SOFA score as being an independent risk factor for mortality.
Conclusion: In summary, the SOFA score can be used to accurately identify mortality after isolated CABG.
Keywords: Cardiorenal syndrome; Coronary artery by pass grafting; Mortality; Sequential organ failure assessment; Society of thoracic surgeons mortality risk.
Figures
References
-
- Siregar S, Groenwold RH, de Mol BA, Speekenbrink RG, Versteegh MI, Brandon Bravo Bruinsma GJ, Bots ML, van der Graaf Y, van Herwerden LA. Evaluation of cardiac surgery mortality rates: 30-day mortality or longer follow-up? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;44(5):875–883. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezt119. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG. The SOFA (sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on sepsis-related problems of the European society of intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous