Rhein exhibits antioxidative effects similar to Rhubarb in a rat model of traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 28264680
- PMCID: PMC5340037
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1655-x
Rhein exhibits antioxidative effects similar to Rhubarb in a rat model of traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: The brain is secondarily harmed by pathological, physiological, and biological reactions that are caused by traumatic brain injury (TBI). Rhein, a significant composition of Rhubarb, is a well-known traditional Chinese treatment method and has a strong oxidation-resisting characteristic, but Rhein's mechanism remains unclear.
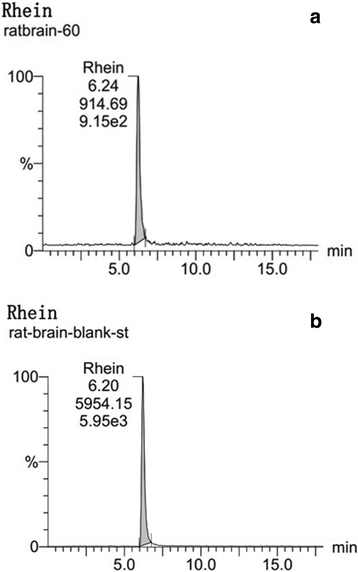
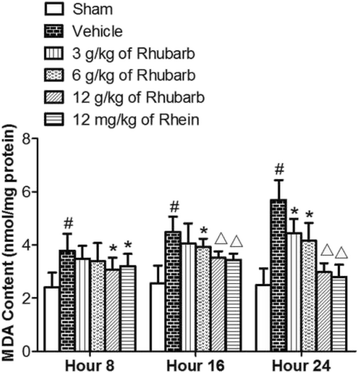
Methods: This study aimed to identify Rhein in the brain tissues of TBI model of rats, and confirm whether Rhein induced an antioxidative effect similar to its parent medicine, Rhubarb. First, the ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method was applied to identify Rhein in the brain tissue of the controlled cortical impact (CCI) rats after intra-gastric administration of Rhubarb. Further, for the purpose of calculating the oxidant stress of the CCI rats, the malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione disulfide (GSSG), as well as the proportion of glutathione (GSH)/GSSG were measured in the brain tissues.
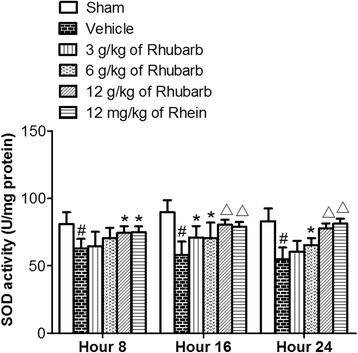
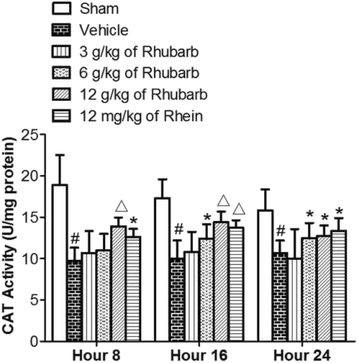
Results: The results showed that Rhein was absorbed in the brain tissues of CCI rats. Rhubarb and rhein elevated the SOD, CAT activities, GSH level, and GSH/GSSG ratio, and diminished the MDA and GSSG levels.
Conclusion: The data demonstrated that Rhubarb and Rhein had the potential to be used as a neuroprotective drug for TBI, and that Rhein induced an antioxidative effect similar to its parent medicine, Rhubarb.
Keywords: Neuroprotective effect; Oxidative stress; Rhein; Rhubarb; Traumatic brain injury.
Figures
References
-
- Toklu, HZ, Tumer N. Oxidative Stress, Brain Edema, Blood-brain Barrier Permeability, and Autonomic Dysfunction from Traumatic Brain Injury, in Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects, F.H. Kobeissy, Editor. Boca Raton (FL): Frontiers in Neuroengineering; 2015.
-
- Laskowski, RA, Creed JA, Raghupathi R. Pathophysiology of Mild TBI: Implications for Altered Signaling Pathways, in Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects, F.H. Kobeissy, Editor. Boca Raton (FL): Frontiers in Neuroengineering; 2015. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

