Efficacy and safety of manual acupuncture manipulations with different frequencies on epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) in functional dyspepsia (FD) patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28264722
- PMCID: PMC5339951
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-1845-3
Efficacy and safety of manual acupuncture manipulations with different frequencies on epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) in functional dyspepsia (FD) patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Manual acupuncture (MA) manipulations are one of the key factors influencing acupuncture effects in traditional Chinese medicine theory. Different MA manipulations contain different stimulating parameters, thus generating different acupuncture responses or effects. Evidence has demonstrated that acupuncture is effective for functional dyspepsia (FD). However, the effects of different stimulating parameters of MA manipulations on FD remain unclear.
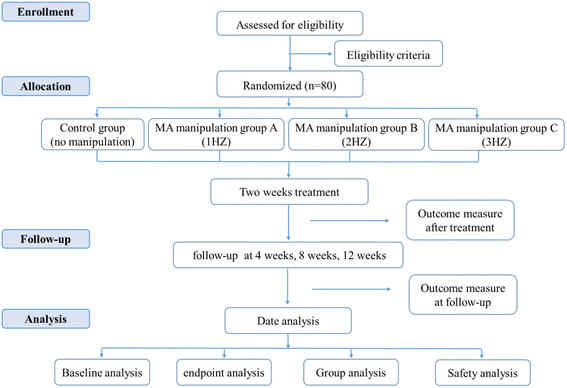
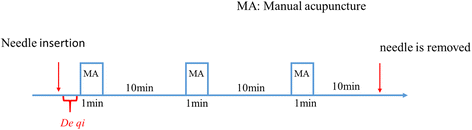
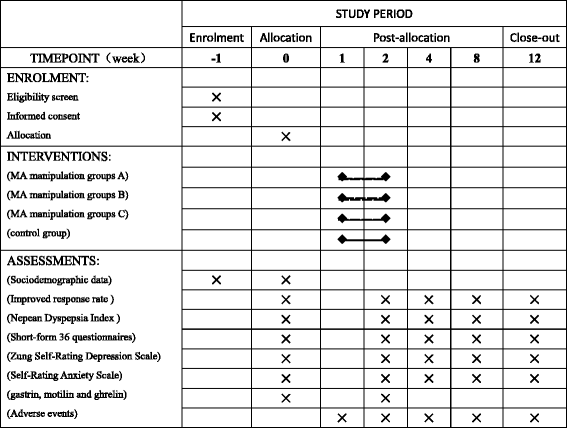
Methods/design: This study is a randomized controlled trial with a four-arm, parallel-group structure. Patients with FD with epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) will be included and randomly allocated into four groups: three MA manipulation groups (separately treated with a frequency of 1 Hz, 2 Hz, or 3 Hz) and a control group. All groups will receive omeprazole as a basic treatment and acupuncture: in the MA manipulation groups, the needles will be manipulated manually with three different frequencies on the basis when de qi is reached, while in the control group, the needles will be inserted without any manipulation. All patients will receive acupuncture treatment of five consecutive sessions per week for 2 weeks and be followed up at 4, 8, and 12 weeks. The primary outcomes of the study include patients' response to the treatment. The secondary outcomes include dyspeptic symptoms, quality of life, mental status, fasting serum gastrin, motilin, and ghrelin concentrations, and adverse events. The protocol was approved by the Ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (2016-K-057-01).
Discussion: The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of MA manipulations with different stimulating parameters (different frequencies) on EPS in patients with FD.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR-IOR-16008189 . Registered on 30 March 2016.
Keywords: Epigastric pain syndrome; Functional dyspepsia; Lifting-inserting; Manipulations; Manual acupuncture.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acupuncture for functional dyspepsia: study protocol for a two-center, randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2014 Mar 22;15:89. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-89. Trials. 2014. PMID: 24655542 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of compatible acupoints and single acupoint versus sham acupuncture for functional dyspepsia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jan 14;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3875-5. Trials. 2020. PMID: 31937335 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acupuncture for postprandial distress syndrome (APDS): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Nov 13;18(1):537. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2285-9. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29132415 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Which subtype of functional dyspepsia patients responses better to acupuncture? A retrospective analysis of a randomized controlled trial.Forsch Komplementmed. 2015;22(2):94-100. doi: 10.1159/000380983. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Forsch Komplementmed. 2015. PMID: 26021959 Review.
-
Electroacupuncture for the treatment of functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 6;99(45):e23014. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023014. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33157947 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Modulates Microbial Phenylalanine Metabolism and Enhances the Intestinal Barrier Function to Alleviate Colitis in Mice.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 14;17:7311-7324. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S472004. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39429851 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromechanism of acupuncture regulating gastrointestinal motility.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 21;26(23):3182-3200. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i23.3182. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32684734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture and moxibustion intervention in functional dyspepsia: Gastric and duodenal regulation.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 6;10(17):e35696. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35696. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Electroacupuncture Treatment with Different Intensities for Functional Diarrhea: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 4;2022:2564979. doi: 10.1155/2022/2564979. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35027932 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of acupuncture intensity on analgesic effects in AA rat models.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 11;12:1502535. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1502535. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39723129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drossman DA, Rome DDL, III New standard for functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006;15:237–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical