Trafficking Ion Transporters to the Apical Membrane of Polarized Intestinal Enterocytes
- PMID: 28264818
- PMCID: PMC5683927
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027979
Trafficking Ion Transporters to the Apical Membrane of Polarized Intestinal Enterocytes
Abstract
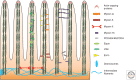
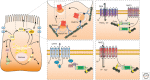
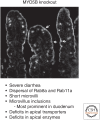
Epithelial cells lining the gastrointestinal tract require distinct apical and basolateral domains to function properly. Trafficking and insertion of enzymes and transporters into the apical brush border of intestinal epithelial cells is essential for effective digestion and absorption of nutrients. Specific critical ion transporters are delivered to the apical brush border to facilitate fluid and electrolyte uptake. Maintenance of these apical transporters requires both targeted delivery and regulated membrane recycling. Examination of altered apical trafficking in patients with Microvillus Inclusion disease caused by inactivating mutations in MYO5B has led to insights into the regulation of apical trafficking by elements of the apical recycling system. Modeling of MYO5B loss in cell culture and animal models has led to recognition of Rab11a and Rab8a as critical regulators of apical brush border function. All of these studies show the importance of apical membrane trafficking dynamics in maintenance of polarized epithelial cell function.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Agbemafle BM, Oesterreicher TJ, Shaw CA, Henning SJ. 2005. Immediate early genes of glucocorticoid action on the developing intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G897–G906. - PubMed
-
- Akhter S, Cavet ME, Tse CM, Donowitz M. 2000. C-terminal domains of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 are involved in the basal and serum-stimulated membrane trafficking of the exchanger. Biochemistry 39: 1990–2000. - PubMed
-
- Alfalah M, Jacob R, Preuss U, Zimmer KP, Naim H, Naim HY. 1999. O-linked glycans mediate apical sorting of human intestinal sucrase-isomaltase through association with lipid rafts. Curr Biol 9: 593–596. - PubMed
-
- Altschuler Y, Hodson C, Milgram SL. 2003. The apical compartment: Trafficking pathways, regulators and scaffolding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15: 423–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
