Contributions of both ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter and Cyp51A Proteins Are Essential for Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 28264842
- PMCID: PMC5404575
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02748-16
Contributions of both ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter and Cyp51A Proteins Are Essential for Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
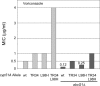
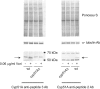
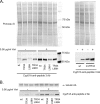
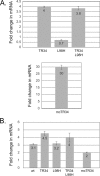
While azole drugs targeting the biosynthesis of ergosterol are effective antifungal agents, their extensive use has led to the development of resistant organisms. Infections involving azole-resistant forms of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus are often associated with genetic changes in the cyp51A gene encoding the lanosterol α14 demethylase target enzyme. Both a sequence duplication in the cyp51A promoter (TR34) and a substitution mutation in the coding sequence (L98H) are required for the full expression of azole resistance. A mechanism commonly observed in pathogenic yeast such as Candida albicans involves gain-of-function mutations in transcriptional regulatory proteins that induce expression of genes encoding ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. We and others have found that an ABC transporter protein called Cdr1B (here referred to as AbcG1) is required for wild-type azole resistance in A. fumigatus Here, we test the genetic relationship between the TR34 L98H allele of cyp51A and an abcG1 null mutation. Loss of AbcG1 from a TR34 L98H cyp51A-containing strain caused a large decrease in the azole resistance of the resulting double-mutant strain. We also generated antibodies that enabled the detection of both the wild-type and L98H forms of the Cyp51A protein. The introduction of the L98H lesion into the cyp51A gene led to a decreased production of immunoreactive enzyme, suggesting that this mutant protein is unstable. Our data confirm the importance of AbcG1 function during azole resistance even in a strongly drug-resistant background.
Keywords: ATP-binding cassette transporter; Aspergillus fumigatus; Western blotting; azole resistance; cyp51A; genetic analysis.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene-specific transcriptional activation by the Aspergillus fumigatus AtrR factor requires a conserved C-terminal domain.mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0042524. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00425-24. Epub 2024 Jul 8. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38975761 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Analysis of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism for Rapid Detection of TR34/L98H- and TR46/Y121F/T289A-Positive Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates Obtained from Patients in Iran from 2010 to 2014.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov 2;60(1):387-92. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02326-15. Print 2016 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26525787 Free PMC article.
-
AtrR Is an Essential Determinant of Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus.mBio. 2019 Mar 12;10(2):e02563-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02563-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30862750 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring azole antifungal drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus with special reference to resistance mechanisms.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(5):697-711. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.27. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24957095 Review.
-
Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus- comprehensive review.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Jun 15;206(7):305. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04026-z. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38878211 Review.
Cited by
-
Voriconazole Treatment Induces a Conserved Sterol/Pleiotropic Drug Resistance Regulatory Network, including an Alternative Ergosterol Biosynthesis Pathway, in the Clinically Important FSSC Species, Fusarium keratoplasticum.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;8(10):1070. doi: 10.3390/jof8101070. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294635 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-specific transcriptional activation by the Aspergillus fumigatus AtrR factor requires a conserved C-terminal domain.mSphere. 2024 Jul 30;9(7):e0042524. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00425-24. Epub 2024 Jul 8. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38975761 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive Fungal Infections in Patients with Hematological Malignancies: Emergence of Resistant Pathogens and New Antifungal Therapies.Turk J Haematol. 2018 Mar 1;35(1):1-11. doi: 10.4274/tjh.2018.0007. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Turk J Haematol. 2018. PMID: 29391334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDR Transporter ABC1 Is Involved in the Innate Azole Resistance of the Human Fungal Pathogen Fusarium keratoplasticum.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 4;12:673206. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.673206. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34149660 Free PMC article.
-
A Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Approach to Track down Genomic Variants in Itraconazole-Resistant Species of Aspergillus from Iran.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;8(10):1091. doi: 10.3390/jof8101091. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howard SJ, Cerar D, Anderson MJ, Albarrag A, Fisher MC, Pasqualotto AC, Laverdiere M, Arendrup MC, Perlin DS, Denning DW. 2009. Frequency and evolution of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus associated with treatment failure. Emerg Infect Dis 15:1068–1076. doi:10.3201/eid1507.090043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Linden JW, Snelders E, Kampinga GA, Rijnders BJ, Mattsson E, Debets-Ossenkopp YJ, Kuijper EJ, Van Tiel FH, Melchers WJ, Verweij PE. 2011. Clinical implications of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus, The Netherlands, 2007–2009. Emerg Infect Dis 17:1846–1854. doi:10.3201/eid1710.110226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Linden JW, Camps SM, Kampinga GA, Arends JP, Debets-Ossenkopp YJ, Haas PJ, Rijnders BJ, Kuijper EJ, van Tiel FH, Varga J, Karawajczyk A, Zoll J, Melchers WJ, Verweij PE. 2013. Aspergillosis due to voriconazole highly resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and recovery of genetically related resistant isolates from domiciles. Clin Infect Dis 57:513–520. doi:10.1093/cid/cit320. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

