In Vivo Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Antofloxacin against Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Neutropenic Murine Lung Infection Model
- PMID: 28264844
- PMCID: PMC5404557
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02691-16
In Vivo Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles of Antofloxacin against Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Neutropenic Murine Lung Infection Model
Abstract
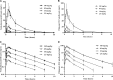
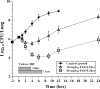
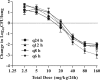
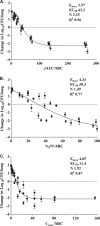
Antofloxacin is a novel broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone under development for the treatment of infections caused by a diverse group of bacterial species. We explored the pharmacodynamic (PD) profile and targets of antofloxacin against seven Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates by using a neutropenic murine lung infection model. Plasma and bronchopulmonary pharmacokinetic (PK) studies were conducted at single subcutaneous doses of 2.5, 10, 40, and 160 mg/kg of body weight. Mice were infected intratracheally with K. pneumoniae and treated using 2-fold-increasing total doses of antofloxacin ranging from 2.5 to 160 mg/kg/24 h administered in 1, 2, 3, or 4 doses. The Emax Hill equation was used to model the dose-response data. Antofloxacin could penetrate the lung epithelial lining fluid (ELF) with pharmacokinetics similar to those in plasma with linear elimination half-lives over the dose range. All study strains showed a 3-log10 or greater reduction in bacterial burden and prolonged postantibiotic effects (PAEs) ranging from 3.2 to 5.3 h. Dose fractionation response curves were steep, and the free-drug area under the concentration-time curve over 24 h (AUC0-24)/MIC ratio was the PD index most closely linked to efficacy (R2 = 0.96). The mean free-drug AUC0-24/MIC ratios required to achieve net bacterial stasis, a 1-log10 kill, and a 2-log10 kill for each isolate were 52.6, 89.9, and 164.9, respectively. When integrated with human PK data, these PD targets could provide a framework for further optimization of dosing regimens. This could make antofloxacin an attractive option for the treatment of respiratory tract infections involving K. pneumoniae.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; PK/PD; antofloxacin; murine lung infection.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Vivo Bioluminescent Monitoring of Therapeutic Efficacy and Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Antofloxacin against Escherichia coli in a Neutropenic Murine Thigh Infection Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Dec 21;62(1):e01281-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01281-17. Print 2018 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 29038275 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Murine Lung Infection Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Jul 22;60(8):4764-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00647-16. Print 2016 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27216072 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of antofloxacin hydrochloride in a neutropenic murine thigh model of Staphylococcus aureus infection.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008 Oct;29(10):1253-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00872.x. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008. PMID: 18817632
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of cefpodoxime: a systematic review.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024 Oct;20(10):989-1001. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2024.2391389. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39120118
-
Seizures associated with ofloxacin therapy.Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Dec;21(6):1504-6. doi: 10.1093/clinids/21.6.1504. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. PMID: 8749646 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Gamithromycin Treatment of Pasteurella multocida in a Murine Lung Infection Model.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 24;10:1090. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01090. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31680940 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enrofloxacin treatment of Escherichia coli in a murine thigh infection modeling.BMC Vet Res. 2021 Jun 9;17(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12917-021-02908-8. BMC Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 34107961 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Antofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus in a Neutropenic Murine Pneumonia Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Nov 17;64(12):e01354-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01354-20. Print 2020 Nov 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32928734 Free PMC article.
-
Microdialysis Determination of Cefquinome Pharmacokinetics in Murine Thigh From Healthy, Neutropenic, and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-Infected Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 12;10:249. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00249. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30914957 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Thigh Microdialysis to Evaluate the Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Integration of Cefquinome Against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Aug 5;7:448. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00448. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32851028 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

