Structural Alteration of OmpR as a Source of Ertapenem Resistance in a CTX-M-15-Producing Escherichia coli O25b:H4 Sequence Type 131 Clinical Isolate
- PMID: 28264855
- PMCID: PMC5404536
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00014-17
Structural Alteration of OmpR as a Source of Ertapenem Resistance in a CTX-M-15-Producing Escherichia coli O25b:H4 Sequence Type 131 Clinical Isolate
Abstract
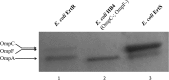
In this study, an ertapenem-nonsusceptible Escherichia coli isolate was investigated to determine the genetic basis for its carbapenem resistance phenotype. This clinical strain was recovered from a patient that received, 1 year previously, ertapenem to treat a cholangitis due to a carbapenem-susceptible extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli isolate. Whole-genome sequencing of these strains was performed using Illumina and single-molecule real-time sequencing technologies. It revealed that they belonged to the ST131 clonal group, had the predicted O25b:H4 serotype, and produced the CTX-M-15 and TEM-1 β-lactamases. One nucleotide substitution was identified between these strains. It affected the ompR gene, which codes for a regulatory protein involved in the control of OmpC/OmpF porin expression, creating a Gly-63-Val substitution. The role of OmpR alteration was confirmed by a complementation experiment that fully restored the susceptibility to ertapenem of the clinical isolate. A modeling study showed that the Gly-63-Val change displaced the histidine-kinase phosphorylation site. SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that the ertapenem-nonsusceptible E. coli strain had a decreased expression of OmpC/OmpF porins. No significant defect in the growth rate or in the resistance to Dictyostelium discoideum amoeba phagocytosis was found in the ertapenem-nonsusceptible E. coli isolate compared to its susceptible parental strain. Our report demonstrates for the first time that ertapenem resistance may emerge clinically from ESBL-producing E. coli due to mutations that modulate the OmpR activity.
Keywords: ESBL; OmpR; ST131; avibactam; carbapenem; envZ; temocillin.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

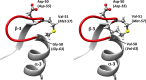

References
-
- Pérez A, Canle D, Latasa C, Poza M, Beceiro A, del Mar Tomás M, Fernández A, Mallo S, Pérez S, Molina F, Villanueva R, Lasa I, Bou G. 2007. Cloning, nucleotide sequencing, and analysis of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump of Enterobacter cloacae and determination of its involvement in antibiotic resistance in a clinical isolate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:3247–3253. doi:10.1128/AAC.00072-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goessens WH, van der Bij AK, van Boxtel R, Pitout JD, van Ulsen P, Melles DC, Tommassen J. 2013. Antibiotic trapping by plasmid-encoded CMY-2 β-lactamase combined with reduced outer membrane permeability as a mechanism of carbapenem resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:3941–3949. doi:10.1128/AAC.02459-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

