Gastrointestinal-Renal Axis: Role in the Regulation of Blood Pressure
- PMID: 28264861
- PMCID: PMC5524043
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005536
Gastrointestinal-Renal Axis: Role in the Regulation of Blood Pressure
Keywords: blood pressure; gastrointestinal tract; hypertension; kidney; salt sensing.
Figures
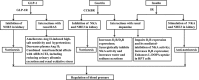
Similar articles
-
The dopaminergic system in hypertension.Clin Sci (Lond). 2007 Jun;112(12):583-97. doi: 10.1042/CS20070018. Clin Sci (Lond). 2007. PMID: 17492945 Review.
-
Central role of the kidney and abnormal fluid volume control in hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 1996 Oct;10(10):633-9. J Hum Hypertens. 1996. PMID: 9004086 Review.
-
Blood pressure variability and the renal response.R I Med. 1993 May;76(5):221-4. R I Med. 1993. PMID: 8518495 Review. No abstract available.
-
Participation of renal and circulating endothelin in salt-sensitive essential hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 2002 Jul;16(7):459-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1001419. J Hum Hypertens. 2002. PMID: 12080429 Review.
-
Blood pressure and renal function after kidney donation from hypertensive living donors.Transplantation. 2005 Jun 27;79(12):1768-9; author reply 1769-70. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000167702.03032.1f. Transplantation. 2005. PMID: 15973187 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Gastrin, via activation of PPARα, protects the kidney against hypertensive injury.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Jan 29;135(2):409-427. doi: 10.1042/CS20201340. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33458737 Free PMC article.
-
DPP-4 Inhibitors: Renoprotective Potential and Pharmacokinetics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Renal Impairment.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Feb;45(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s13318-019-00570-y. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31385198 Review.
-
Increased oral sodium chloride intake in humans amplifies selectively postprandial GLP-1 but not GIP, CCK, and gastrin in plasma.Physiol Rep. 2020 Aug;8(15):e14519. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14519. Physiol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32770661 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inhibition of sodium-proton-exchanger subtype 3-mediated sodium absorption in the gut: A new antihypertensive concept.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2020 Jul 23;29:100591. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2020.100591. eCollection 2020 Aug. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2020. PMID: 32760780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pien Tze Huang (PZH) as a Multifunction Medicinal Agent in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM): a review on cellular, molecular and physiological mechanisms.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Mar 3;21(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01785-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33658028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Poulter NR, Prabhakaran D, Caulfield M. Hypertension. Lancet. 2015;386:801–812. - PubMed
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Appel LJ, Sacco RL, Anderson CA, Antman EM, Campbell N, Dunbar SB, Frohlich ED, Hall JE, Jessup M, Labarthe DR, MacGregor GA, Sacks FM, Stamler J, Vafiadis DK, Van Horn LV. Sodium, blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease: further evidence supporting the American Heart Association sodium reduction recommendations. Circulation. 2012;126:2880–2889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

