Inflammatory monocytes require type I interferon receptor signaling to activate NK cells via IL-18 during a mucosal viral infection
- PMID: 28264883
- PMCID: PMC5379971
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20160880
Inflammatory monocytes require type I interferon receptor signaling to activate NK cells via IL-18 during a mucosal viral infection
Abstract
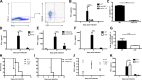
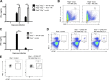
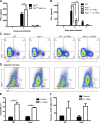
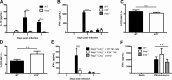
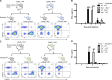
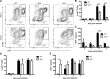
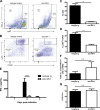
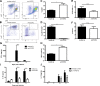
The requirement of type I interferon (IFN) for natural killer (NK) cell activation in response to viral infection is known, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that type I IFN signaling in inflammatory monocytes, but not in dendritic cells (DCs) or NK cells, is essential for NK cell function in response to a mucosal herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) infection. Mice deficient in type I IFN signaling, Ifnar-/- and Irf9-/- mice, had significantly lower levels of inflammatory monocytes, were deficient in IL-18 production, and lacked NK cell-derived IFN-γ. Depletion of inflammatory monocytes, but not DCs or other myeloid cells, resulted in lower levels of IL-18 and a complete abrogation of NK cell function in HSV-2 infection. Moreover, this resulted in higher susceptibility to HSV-2 infection. Although Il18-/- mice had normal levels of inflammatory monocytes, their NK cells were unresponsive to HSV-2 challenge. This study highlights the importance of type I IFN signaling in inflammatory monocytes and the induction of the early innate antiviral response.
© 2017 Lee et al.
Figures
References
-
- Baranek T., Manh T.P., Alexandre Y., Maqbool M.A., Cabeza J.Z., Tomasello E., Crozat K., Bessou G., Zucchini N., Robbins S.H., et al. 2012. Differential responses of immune cells to type I interferon contribute to host resistance to viral infection. Cell Host Microbe. 12:571–584 (published erratum appears in Cell Host Microbe 2013. 13:372) . 10.1016/j.chom.2012.09.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barr D.P., Belz G.T., Reading P.C., Wojtasiak M., Whitney P.G., Heath W.R., Carbone F.R., and Brooks A.G.. 2007. A role for plasmacytoid dendritic cells in the rapid IL-18-dependent activation of NK cells following HSV-1 infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 37:1334–1342. 10.1002/eji.200636362 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

