The agouti-related peptide binds heparan sulfate through segments critical for its orexigenic effects
- PMID: 28264929
- PMCID: PMC5418061
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.772822
The agouti-related peptide binds heparan sulfate through segments critical for its orexigenic effects
Abstract
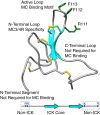
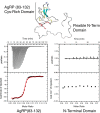
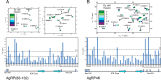
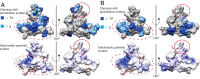
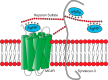
Syndecans potently modulate agouti-related peptide (AgRP) signaling in the central melanocortin system. Through heparan sulfate moieties, syndecans are thought to anchor AgRP near its receptor, enhancing its orexigenic effects. Original work proposed that the N-terminal domain of AgRP facilitates this interaction. However, this is not compatible with evidence that this domain is posttranslationally cleaved. Addressing this long-standing incongruity, we used calorimetry and magnetic resonance to probe interactions of AgRP peptides with glycosaminoglycans, including heparan sulfate. We show that mature, cleaved, C-terminal AgRP, not the N-terminal domain, binds heparan sulfate. NMR shows that the binding site consists of regions distinct from the melanocortin receptor-binding site. Using a library of designed AgRP variants, we find that the strength of the syndecan interaction perfectly tracks orexigenic action. Our data provide compelling evidence that AgRP is a heparan sulfate-binding protein and localizes critical regions in the AgRP structure required for this interaction.
Keywords: AgRP; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); glycosaminoglycan; heparan sulfate; heparin-binding protein; mc4r; neuropeptide; syndecan.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
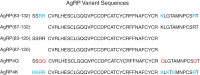


Similar articles
-
Agouti-related protein is posttranslationally cleaved by proprotein convertase 1 to generate agouti-related protein (AGRP)83-132: interaction between AGRP83-132 and melanocortin receptors cannot be influenced by syndecan-3.Endocrinology. 2006 Apr;147(4):1621-31. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1373. Epub 2005 Dec 29. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16384863
-
Structure activity studies of the melanocortin-4 receptor by in vitro mutagenesis: identification of agouti-related protein (AGRP), melanocortin agonist and synthetic peptide antagonist interaction determinants.Biochemistry. 2001 May 22;40(20):6164-79. doi: 10.1021/bi010025q. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11352754
-
Biased signaling initiated by agouti-related peptide through human melanocortin-3 and -4 receptors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1862(9):1485-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 May 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27208795
-
Loops and links: structural insights into the remarkable function of the agouti-related protein.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Jun;994:27-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03159.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12851295 Review.
-
Agouti-related protein: more than a melanocortin-4 receptor antagonist?Peptides. 2005 Oct;26(10):1759-70. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.11.036. Peptides. 2005. PMID: 15996791 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Deletion of Syndecan-4 Alters Body Composition, Metabolic Phenotypes, and the Function of Metabolic Tissues in Female Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 18;11(11):2810. doi: 10.3390/nu11112810. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31752080 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecans modulate ghrelin receptor signaling.J Mol Endocrinol. 2024 Dec 19;74(1):e240070. doi: 10.1530/JME-24-0070. Print 2025 Jan 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39565158 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of glycosaminoglycans in GPCR signaling.Cell Signal. 2024 Jun;118:111149. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111149. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38522808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Charge Characteristics of Agouti-Related Protein Implicate Potent Involvement of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Metabolic Function.iScience. 2019 Dec 20;22:557-570. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.10.061. Epub 2019 Oct 31. iScience. 2019. PMID: 31863782 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Orexigenic Neuropeptides Targeting G Protein-Coupled Receptors.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jun 20;9(6):1235-1246. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00151. Epub 2018 May 11. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29714060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Denis R. G., Joly-Amado A., Webber E., Langlet F., Schaeffer M., Padilla S. L., Cansell C., Dehouck B., Castel J., Delbès A.-S., Martinez S., Lacombe A., Rouch C., Kassis N., Fehrentz J.-A., et al. (2015) Palatability can drive feeding independent of AgRP neurons. Cell Metab. 22, 646–657 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

