Endogenous and xenobiotic metabolic stability of primary human hepatocytes in long-term 3D spheroid cultures revealed by a combination of targeted and untargeted metabolomics
- PMID: 28264975
- PMCID: PMC5434660
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201601375R
Endogenous and xenobiotic metabolic stability of primary human hepatocytes in long-term 3D spheroid cultures revealed by a combination of targeted and untargeted metabolomics
Abstract
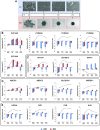
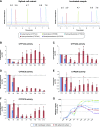
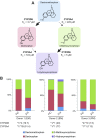
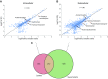
Adverse reactions or lack of response to medications are important concerns for drug development programs. However, faithful predictions of drug metabolism and toxicity are difficult because animal models show only limited translatability to humans. Furthermore, current in vitro systems, such as hepatic cell lines or primary human hepatocyte (PHH) 2-dimensional (2D) monolayer cultures, can be used only for acute toxicity tests because of their immature phenotypes and inherent instability. Therefore, the migration to novel phenotypically stable models is of prime importance for the pharmaceutical industry. Novel 3-dimensional (3D) culture systems have been shown to accurately mimic in vivo hepatic phenotypes on transcriptomic and proteomic level, but information about their metabolic stability is lacking. Using a combination of targeted and untargeted high-resolution mass spectrometry, we found that PHHs in 3D spheroid cultures remained metabolically stable for multiple weeks, whereas metabolic patterns of PHHs from the same donors cultured as conventional 2D monolayers rapidly deteriorated. Furthermore, pharmacokinetic differences between donors were maintained in 3D spheroid cultures, enabling studies of interindividual variability in drug metabolism and toxicity. We conclude that the 3D spheroid system is metabolically stable and constitutes a suitable model for in vitro studies of long-term drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics.-Vorrink, S. U., Ullah, S., Schmid, S., Nandania, J., Velagapudi, V., Beck, O., Ingelman-Sundberg, M., Lauschke, V. M. Endogenous and xenobiotic metabolic stability of primary human hepatocytes in long-term 3D spheroid cultures revealed by a combination of targeted and untargeted metabolomics.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; cytochrome P450 enzymes; drug metabolism; hepatic metabolism; mass spectrometry.
© The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 23;8(10):374. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100374. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32977664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three-Dimensional Spheroid Primary Human Hepatocytes in Monoculture and Coculture with Nonparenchymal Cells.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2018 Sep;24(9):534-545. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2018.0134. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2018. PMID: 30101670
-
From the Cover: Three-Dimensional (3D) HepaRG Spheroid Model With Physiologically Relevant Xenobiotic Metabolism Competence and Hepatocyte Functionality for Liver Toxicity Screening.Toxicol Sci. 2017 Sep 1;159(1):124-136. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx122. Toxicol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28633424 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Hepatic 2D Sandwich Cultures and 3D Spheroids for Long-term Toxicity Applications: A Multicenter Study.Toxicol Sci. 2018 Apr 1;162(2):655-666. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx289. Toxicol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29329425 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Liver Culture Systems to Maintain Primary Hepatic Properties for Toxicological Analysis In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 23;22(19):10214. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910214. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638555 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microphysiological Drug-Testing Platform for Identifying Responses to Prodrug Treatment in Primary Leukemia.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 Jan;12(6):e2202506. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202202506. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36651229 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Evaluation of Organotypic and Microphysiological Liver Models for Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Injury.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 24;10:1093. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01093. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31616302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of Three-Dimensional Cultures of Primary Human Hepatocytes (Spheroids) as Pharmacokinetic Models.Biomedicines. 2020 Sep 23;8(10):374. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100374. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 32977664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenoconversion of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2020 Sep 7;9(9):2890. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092890. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32906709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Perspective on 3D Liver Models for Drug Metabolism and Toxicology Studies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 22;9:626805. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.626805. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33732695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Björnsson E. S., Bergmann O. M., Björnsson H. K., Kvaran R. B., Olafsson S. (2013) Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology 144, 1419–1425.e3; quiz e19–e20 - PubMed
-
- Sgro C., Clinard F., Ouazir K., Chanay H., Allard C., Guilleminet C., Lenoir C., Lemoine A., Hillon P. (2002) Incidence of drug-induced hepatic injuries: a French population-based study. Hepatology 36, 451–455 - PubMed
-
- Björnsson E., Olsson R. (2005) Outcome and prognostic markers in severe drug-induced liver disease. Hepatology 42, 481–489 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

