A PTEN-Regulated Checkpoint Controls Surface Delivery of δ Opioid Receptors
- PMID: 28264976
- PMCID: PMC5394893
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2923-16.2017
A PTEN-Regulated Checkpoint Controls Surface Delivery of δ Opioid Receptors
Abstract
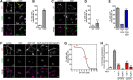
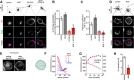
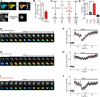
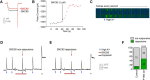
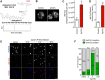
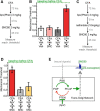
The δ opioid receptor (δR) is a promising alternate target for pain management because δR agonists show decreased abuse potential compared with current opioid analgesics that target the μ opioid receptor. A critical limitation in developing δR as an analgesic target, however, is that δR agonists show relatively low efficacy in vivo, requiring the use of high doses that often cause adverse effects, such as convulsions. Here we tested whether intracellular retention of δR in sensory neurons contributes to this low δR agonist efficacy in vivo by limiting surface δR expression. Using direct visualization of δR trafficking and localization, we define a phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-regulated checkpoint that retains δR in the Golgi and decreases surface delivery in rat and mice sensory neurons. PTEN inhibition releases δR from this checkpoint and stimulates delivery of exogenous and endogenous δR to the neuronal surface both in vitro and in vivo PTEN inhibition in vivo increases the percentage of TG neurons expressing δR on the surface and allows efficient δR-mediated antihyperalgesia in mice. Together, we define a critical role for PTEN in regulating the surface delivery and bioavailability of the δR, explain the low efficacy of δR agonists in vivo, and provide evidence that active δR relocation is a viable strategy to increase δR antinociception.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Opioid analgesics, such as morphine, which target the μ opioid receptor (μR), have been the mainstay of pain management, but their use is highly limited by adverse effects and their variable efficacy in chronic pain. Identifying alternate analgesic targets is therefore of great significance. Although the δ opioid receptor (δR) is an attractive option, a critical limiting factor in developing δR as a target has been the low efficacy of δR agonists. Why δR agonists show low efficacy is still under debate. This study provides mechanistic and functional data that intracellular localization of δR in neurons is a key factor that contributes to low agonist efficacy, and presents a proof of mechanism that relocating δR improves efficacy.
Keywords: Golgi export; exocytosis; nociception; opioid; trafficking.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/373741-12$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3K class II α regulates δ-opioid receptor export from the trans-Golgi network.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Aug 1;28(16):2202-2219. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-01-0030. Epub 2017 May 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28566554 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin-regulated sorting of opioid receptors in the biosynthetic pathway of neurosecretory cells.J Neurosci. 2003 Mar 15;23(6):2075-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-06-02075.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12657666 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of the 6-O-sulfate ester of morphine in normal and diabetic rats: Comparative role of mu- and delta-opioid receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):335-347. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27637375 Free PMC article.
-
Delta and kappa opioid receptors as suitable drug targets for pain.Clin J Pain. 2010 Jan;26 Suppl 10:S10-5. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181c49e3a. Clin J Pain. 2010. PMID: 20026960 Review.
-
Role of delivery and trafficking of delta-opioid peptide receptors in opioid analgesia and tolerance.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Jun;27(6):324-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 May 6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16678916 Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution of functional opioid receptors in human dorsal root ganglion neurons.Pain. 2020 Jul;161(7):1636-1649. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001846. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32102022 Free PMC article.
-
Control of CCR5 Cell-Surface Targeting by the PRAF2 Gatekeeper.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 13;24(24):17438. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417438. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139265 Free PMC article.
-
Potassium-regulated distal tubule WNK bodies are kidney-specific WNK1 dependent.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Feb 15;29(4):499-509. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-08-0529. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29237822 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational specificity of opioid receptors is determined by subcellular location irrespective of agonist.Elife. 2021 May 20;10:e67478. doi: 10.7554/eLife.67478. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34013886 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and specificity in location-based signaling outputs of neuronal GPCRs.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;76:102601. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102601. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35797808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balla T, Wymann M, York JD (2012) Phosphoinositides I: Enzymes of synthesis and degradation. New York: Springer.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
