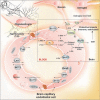
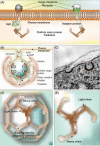
Blood-brain barrier transport machineries and targeted therapy of brain diseases
- PMID: 28265539
- PMCID: PMC5326671
- DOI: 10.15171/bi.2016.30
Blood-brain barrier transport machineries and targeted therapy of brain diseases
Abstract
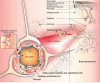
Introduction: Desired clinical outcome of pharmacotherapy of brain diseases largely depends upon the safe drug delivery into the brain parenchyma. However, due to the robust blockade function of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), drug transport into the brain is selectively controlled by the BBB formed by brain capillary endothelial cells and supported by astrocytes and pericytes. Methods: In the current study, we have reviewed the most recent literature on the subject to provide an insight upon the role and impacts of BBB on brain drug delivery and targeting. Results: All drugs, either small molecules or macromolecules, designated to treat brain diseases must adequately cross the BBB to provide their therapeutic properties on biological targets within the central nervous system (CNS). However, most of these pharmaceuticals do not sufficiently penetrate into CNS, failing to meet the intended therapeutic outcomes. Most lipophilic drugs capable of penetrating BBB are prone to the efflux functionality of BBB. In contrast, all hydrophilic drugs are facing severe infiltration blockage imposed by the tight cellular junctions of the BBB. Hence, a number of strategies have been devised to improve the efficiency of brain drug delivery and targeted therapy of CNS disorders using multimodal nanosystems (NSs). Conclusions: In order to improve the therapeutic outcomes of CNS drug transfer and targeted delivery, the discriminatory permeability of BBB needs to be taken under control. The carrier-mediated transport machineries of brain capillary endothelial cells (BCECs) can be exploited for the discovery, development and delivery of small molecules into the brain. Further, the receptor-mediated transport systems can be recruited for the delivery of macromolecular biologics and multimodal NSs into the brain.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Brain diseases; Brain drug delivery; Brain drug targeting; Carrier-mediated transport; Endocytosis; Receptor-mediated transport, Transcytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impacts of blood-brain barrier in drug delivery and targeting of brain tumors.Bioimpacts. 2012;2(1):5-22. doi: 10.5681/bi.2012.002. Epub 2012 Feb 2. Bioimpacts. 2012. PMID: 23678437 Free PMC article.
-
Getting into the brain: approaches to enhance brain drug delivery.CNS Drugs. 2009;23(1):35-58. doi: 10.2165/0023210-200923010-00003. CNS Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19062774 Review.
-
Brain penetrating peptides and peptide-drug conjugates to overcome the blood-brain barrier and target CNS diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2021 Jul;13(4):e1695. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1695. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33470550 Review.
-
Targeting receptor-ligand chemistry for drug delivery across blood-brain barrier in brain diseases.Life Sci. 2021 Jun 1;274:119326. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119326. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33711385 Review.
-
Blood-brain barrier drug discovery for central nervous system infections.Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2005 Mar;5(1):65-72. doi: 10.2174/1568005053174672. Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. 2005. PMID: 15777199 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain organoid-on-a-chip: A next-generation human brain avatar for recapitulating human brain physiology and pathology.Biomicrofluidics. 2022 Nov 23;16(6):061301. doi: 10.1063/5.0121476. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biomicrofluidics. 2022. PMID: 36438549 Free PMC article.
-
Latest Perspectives on Alzheimer's Disease Treatment: The Role of Blood-Brain Barrier and Antioxidant-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Molecules. 2024 Aug 27;29(17):4056. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174056. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and considerations in AD tau-targeted immunotherapy.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Feb;134:104707. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104707. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31841678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of hypoxia on blood-brain, blood-CSF, and CSF-brain barriers.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021 Sep 1;131(3):977-985. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00108.2020. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021. PMID: 34264124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-dependent redox status in the brain stem of NO-deficient hypertensive rats.J Biomed Sci. 2017 Sep 11;24(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12929-017-0366-4. J Biomed Sci. 2017. PMID: 28893245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources