Anti-inflammatory effect of Fumaria parviflora leaves based on TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 and antioxidant potential
- PMID: 28265545
- PMCID: PMC5329175
Anti-inflammatory effect of Fumaria parviflora leaves based on TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 and antioxidant potential
Abstract
Objective: In this study, we evaluated anti-inflammatory activity of leaves of Fumaria parviflora (F. parviflora) and underlying mechanisms by using in vivo models of inflammation.
Material and methods: Albino Wistar rats of either sex weighing 150 - 200 g were used. Soxhlet ethanol and aqueous extracts of leaves of F. parviflora (EFP and AFP) were prepared. The anti-inflammatory activity was studied using carrageenan-induced paw edema method and cotton pellet granuloma method. Levels of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1 and activity of antioxidant enzymes including catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were estimated.
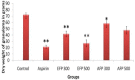
Results: Leaves of F. parviflora demonstrated significant (p<0.001) decrease in paw edema in carrageenan-induced paw edema method. It diminished the serum tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-6 and IL-1 levels and also significantly attenuated the malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. The activity of CAT and GPx was increased in paw tissue. It also demonstrated significant decrease in granuloma formation in cotton pellet-induced granuloma method.
Conclusion: Leaves of F. parviflora possess anti-inflammatory activity as they inhibit various cytokines and have antioxidant effects and free radical scavenging activity.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Antioxidant; Carrageenan; Cytokines; Fumeria parviflora.
Figures


References
-
- Amin GH. Popular Medical Plants of Iran. Tehran: Farhang Publication; 1991. pp. 51–2.
-
- Armstrong D, Browne R. The analysis of free radicals, lipid peroxides, antioxidant enzymes and compounds related to oxidative stress as applied to the clinical chemistry laboratory. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;366:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Bignotto L, Rocha J, Sepodes B, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of lycopene on carrageenan-induced paw oedema and hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion in the rat. Br J Nutr. 2009;102:126–33. - PubMed
-
- Chang CT, Huang SS, Lin SS. Anti-inflammatory activities of tormentic acid from suspension cells of Eriobotrya japonica ex vivo and in vivo. Food Chem. 2011;127:1131–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
