Identifying ionic interactions within a membrane using BLaTM, a genetic tool to measure homo- and heterotypic transmembrane helix-helix interactions
- PMID: 28266525
- PMCID: PMC5339904
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43476
Identifying ionic interactions within a membrane using BLaTM, a genetic tool to measure homo- and heterotypic transmembrane helix-helix interactions
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Identifying ionic interactions within a membrane using BLaTM, a genetic tool to measure homo- and heterotypic transmembrane helix-helix interactions.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 24;10(1):7223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63947-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32332822 Free PMC article.
Abstract
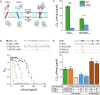
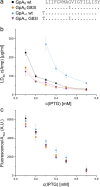
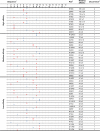
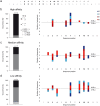
The assembly of integral membrane protein complexes is frequently supported by transmembrane domain (TMD) interactions. Here, we present the BLaTM assay that measures homotypic as well as heterotypic TMD-TMD interactions in a bacterial membrane. The system is based on complementation of β-lactamase fragments genetically fused to interacting TMDs, which confers ampicillin resistance to expressing cells. We validated BLaTM by showing that the assay faithfully reports known sequence-specific interactions of both types. In a practical application, we used BLaTM to screen a focussed combinatorial library for heterotypic interactions driven by electrostatic forces. The results reveal novel patterns of ionizable amino acids within the isolated TMD pairs. Those patterns indicate that formation of heterotypic TMD pairs is most efficiently supported by closely spaced ionizable residues of opposite charge. In addition, TMD heteromerization can apparently be driven by hydrogen bonding between basic or between acidic residues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Neumann J., Klein N., Otzen D. E. & Schneider D. Folding energetics and oligomerization of polytopic alpha-helical transmembrane proteins. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 564, 281–296 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Cymer F., Veerappan A. & Schneider D. Transmembrane helix-helix interactions are modulated by the sequence context and by lipid bilayer properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818, 963–973 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Teese M. G. & Langosch D. Role of GxxxG Motifs in Transmembrane Domain Interactions. Biochemistry 54, 5125–5135 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Fink A., Sal-Man N., Gerber D. & Shai Y. Transmembrane domains interactions within the membrane milieu: Principles, advances and challenges. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1818, 974–983 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

