Ablation of neuropsin-neuregulin 1 signaling imbalances ErbB4 inhibitory networks and disrupts hippocampal gamma oscillation
- PMID: 28267150
- PMCID: PMC5416666
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2017.20
Ablation of neuropsin-neuregulin 1 signaling imbalances ErbB4 inhibitory networks and disrupts hippocampal gamma oscillation
Abstract
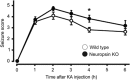
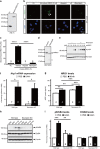
Parvalbumin-expressing interneurons are pivotal for the processing of information in healthy brain, whereas the coordination of these functions is seriously disrupted in diseased brain. How these interneurons in the hippocampus participate in pathological functions remains unclear. We previously reported that neuregulin 1 (NRG1)-ErbB4 signaling, which is actuated by neuropsin, is important for coordinating brain plasticity. Neuropsin cleaves mature NRG1 (bound to extracellular glycosaminoglycans) in response to long-term potentiation or depression, liberating a soluble ligand that activates its receptor, ErbB4. Here, we show in mice that kainate-induced status epilepticus transiently elevates the proteolytic activity of neuropsin and stimulates cFos expression with a time course suggesting that activation of ErbB4- and parvalbumin-expressing interneurons follows the excitation and subsequent silencing of pyramidal neurons. In neuropsin-deficient mice, kainate administration impaired signaling and disrupted the neuronal excitation-inhibition balance (E/I balance) in hippocampal networks, by decreasing the activity of parvalbumin-positive interneurons while increasing that of pyramidal neurons, resulting in the progression of status epilepticus. Slow, but not fast, gamma oscillations in neuropsin-deficient mice showed reduced power. Intracerebroventricular infusion of the soluble NRG1 ligand moiety restored the E/I balance, status epilepticus and gamma oscillations to normal levels. These results suggest that the neuropsin-NRG1 signaling system has a role in pathological processes underlying temporal lobe epilepsy by regulating the activity of parvalbumin-expressing interneurons, and that neuropsin regulates E/I balance and gamma oscillations through NRG1-ErbB4 signaling toward parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. This neuronal system may be a useful target of pharmacological therapies against cognitive disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

