Favorable Neurocognitive Outcome with Low Tidal Volume Ventilation after Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 28267376
- PMCID: PMC5439016
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201609-1771OC
Favorable Neurocognitive Outcome with Low Tidal Volume Ventilation after Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
Rationale: Neurocognitive outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is often poor, even when initial resuscitation succeeds. Lower tidal volumes (Vts) attenuate extrapulmonary organ injury in other disease states and are neuroprotective in preclinical models of critical illness.
Objective: To evaluate the association between Vt and neurocognitive outcome after OHCA.
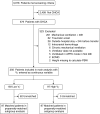
Methods: We performed a propensity-adjusted analysis of a two-center retrospective cohort of patients experiencing OHCA who received mechanical ventilation for at least the first 48 hours of hospitalization. Vt was calculated as the time-weighted average over the first 48 hours, in milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight (PBW). The primary endpoint was favorable neurocognitive outcome (cerebral performance category of 1 or 2) at discharge.
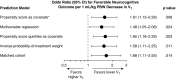
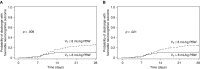
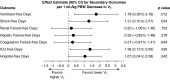
Measurements and main results: Of 256 included patients, 38% received time-weighted average Vt greater than 8 ml/kg PBW during the first 48 hours. Lower Vt was independently associated with favorable neurocognitive outcome in propensity-adjusted analysis (odds ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13-2.28 per 1-ml/kg PBW decrease in Vt; P = 0.008). This finding was robust to several sensitivity analyses. Lower Vt also was associated with more ventilator-free days (β = 1.78; 95% CI, 0.39-3.16 per 1-ml/kg PBW decrease; P = 0.012) and shock-free days (β = 1.31; 95% CI, 0.10-2.51; P = 0.034). Vt was not associated with hypercapnia (P = 1.00). Although the propensity score incorporated several biologically relevant covariates, only height, weight, and admitting hospital were independent predictors of Vt less than or equal to 8 ml/kg PBW.
Conclusions: Lower Vt after OHCA is independently associated with favorable neurocognitive outcome, more ventilator-free days, and more shock-free days. These findings suggest a role for low-Vt ventilation after cardiac arrest.
Keywords: acute lung injury; cardiac arrest; cerebral ischemia; out-of-hospital cardiac arrest; ventilator-induced lung injury.
Figures
Comment in
-
Lung-Brain Interaction after Cardiac Arrest?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 May 1;195(9):1127-1128. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201703-0611ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28459318 No abstract available.
References
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129:e28–e292. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fugate JE, Brinjikji W, Mandrekar JN, Cloft HJ, White RD, Wijdicks EFM, Rabinstein AA. Post-cardiac arrest mortality is declining: a study of the US National Inpatient Sample 2001 to 2009. Circulation. 2012;126:546–550. - PubMed
-
- Moulaert VRMP, Verbunt JA, van Heugten CM, Wade DT. Cognitive impairments in survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Resuscitation. 2009;80:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Adrie C, Adib-Conquy M, Laurent I, Monchi M, Vinsonneau C, Fitting C, Fraisse F, Dinh-Xuan AT, Carli P, Spaulding C, et al. Successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest as a “sepsis-like” syndrome. Circulation. 2002;106:562–568. - PubMed
-
- Neumar RW, Nolan JP, Adrie C, Aibiki M, Berg RA, Böttiger BW, Callaway C, Clark RSB, Geocadin RG, Jauch EC, et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication. A consensus statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, European Resuscitation Council, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Asia, and the Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa); the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; and the Stroke Council. Circulation. 2008;118:2452–2483. - PubMed

