Thymic NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates CD4+ T cell-elicited liver injury and fibrosis in mice
- PMID: 28267623
- PMCID: PMC5476485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.025
Thymic NF-κB-inducing kinase regulates CD4+ T cell-elicited liver injury and fibrosis in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: The liver is an immunologically-privileged organ. Breakdown of liver immune privilege has been reported in chronic liver disease; however, the role of adaptive immunity in liver injury is poorly defined. Nuclear factor-κB-inducing kinase (NIK) is known to regulate immune tissue development, but its role in maintaining liver homeostasis remains unknown. This study aimed to assess the role of NIK, particularly thymic NIK, in regulating liver adaptive immunity.
Methods: NIK was deleted systemically or conditionally using the Cre/loxp system. Cluster of differentiation [CD]4+ or CD8+ T cells were depleted using anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 antibody. Donor bone marrows or thymi were transferred into recipient mice. Immune cells were assessed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry.
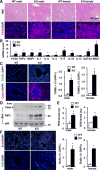
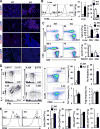
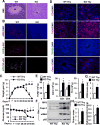
Results: Global, but not liver-specific or hematopoietic lineage cell-specific, deletion of NIK induced fatal liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis. Likewise, adoptive transfer of NIK-null, but not wild-type, thymi into immune-deficient mice induced liver inflammation, injury, and fibrosis in recipients. Liver inflammation was characterized by a massive expansion of T cells, particularly the CD4+ T cell subpopulation. Depletion of CD4+, but not CD8+, T cells fully protected against liver injury, inflammation, and fibrosis in NIK-null mice. NIK deficiency also resulted in inflammation in the lung, kidney, and pancreas, but to a lesser degree relative to the liver.
Conclusions: Thymic NIK suppresses development of autoreactive T cells against liver antigens, and NIK deficiency in the thymus results in CD4+ T cell-orchestrated autoimmune hepatitis and liver fibrosis. Thus, thymic NIK is essential for the maintenance of liver immune privilege and liver homeostasis.
Lay summary: We found that global or thymus-specific ablation of the NIK gene results in fatal autoimmune liver disease in mice. NIK-deficient mice develop liver inflammation, injury, and fibrosis. Our findings indicate that thymic NIK is essential for the maintenance of liver integrity and homeostasis.
Keywords: CD4-positive T-lymphocytes; Flow Cytometry; Hepatitis, autoimmune; Inflammation; Liver cirrhosis; Liver disease; Liver fibrosis; Liver injury.
Copyright © 2017 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Medullary thymic epithelial NF-kB-inducing kinase (NIK)/IKKα pathway shapes autoimmunity and liver and lung homeostasis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 17;116(38):19090-19097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901056116. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31481626 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-intrinsic role for NF-kappa B-inducing kinase in peripheral maintenance but not thymic development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 20;8(9):e76216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076216. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24073289 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappa B-inducing kinase establishes self-tolerance in a thymic stroma-dependent manner.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 15;172(4):2067-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2067. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14764671
-
NIK as a Druggable Mediator of Tissue Injury.Trends Mol Med. 2019 Apr;25(4):341-360. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Trends Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30926358 Review.
-
Priming and Maintenance of Adaptive Immunity in the Liver.Annu Rev Immunol. 2024 Jun;42(1):375-399. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-090122-041354. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Annu Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38360545 Review.
Cited by
-
Fas/FasL mediates NF-κBp65/PUMA-modulated hepatocytes apoptosis via autophagy to drive liver fibrosis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 May 12;12(5):474. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03749-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33980818 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and Prospects of Non-Canonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the Regulation of Liver Diseases.Molecules. 2022 Jul 2;27(13):4275. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134275. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medullary thymic epithelial NF-kB-inducing kinase (NIK)/IKKα pathway shapes autoimmunity and liver and lung homeostasis in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 17;116(38):19090-19097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901056116. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31481626 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate mouse liver fibrosis by inhibiting pathogenic function of intrahepatic B cells.Hepatology. 2025 Apr 1;81(4):1211-1227. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000831. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Hepatology. 2025. PMID: 38546278 Free PMC article.
-
EP3 enhances adhesion and cytotoxicity of NK cells toward hepatic stellate cells in a murine liver fibrosis model.J Exp Med. 2022 May 2;219(5):e20212414. doi: 10.1084/jem.20212414. Epub 2022 Apr 14. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35420633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsuneyama K, Baba H, Kikuchi K, Nishida T, Nomoto K, Hayashi S, Miwa S, et al. Autoimmune features in metabolic liver disease: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013;45:143–148. - PubMed
-
- Lemmers A, Moreno C, Gustot T, Marechal R, Degre D, Demetter P, de Nadai P, et al. The interleukin-17 pathway is involved in human alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2009;49:646–657. - PubMed
-
- Cao Q, Batey R, Pang G, Clancy R. Altered T-lymphocyte responsiveness to polyclonal cell activators is responsible for liver cell necrosis in alcohol-fed rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998;22:723–729. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

