International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. C. Nomenclature and Properties of Calcium-Activated and Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels
- PMID: 28267675
- PMCID: PMC11060434
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.116.012864
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. C. Nomenclature and Properties of Calcium-Activated and Sodium-Activated Potassium Channels
Abstract
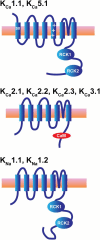
A subset of potassium channels is regulated primarily by changes in the cytoplasmic concentration of ions, including calcium, sodium, chloride, and protons. The eight members of this subfamily were originally all designated as calcium-activated channels. More recent studies have clarified the gating mechanisms for these channels and have documented that not all members are sensitive to calcium. This article describes the molecular relationships between these channels and provides an introduction to their functional properties. It also introduces a new nomenclature that differentiates between calcium- and sodium-activated potassium channels.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Adelman JP, Maylie J, Sah P. (2012) Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels: form and function. Annu Rev Physiol 74:245–269. - PubMed
-
- Adelman JP, Shen KZ, Kavanaugh MP, Warren RA, Wu YN, Lagrutta A, Bond CT, North RA. (1992) Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron 9:209–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases