Ex vivo modulation of the Foxo1 phosphorylation state does not lead to dysfunction of T regulatory cells
- PMID: 28267764
- PMCID: PMC5340387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173386
Ex vivo modulation of the Foxo1 phosphorylation state does not lead to dysfunction of T regulatory cells
Abstract
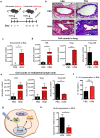
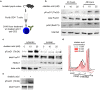
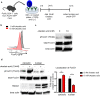
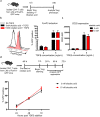
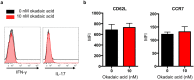
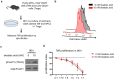
Peripheral regulatory CD4+ T cells (Treg cells) prevent maladaptive inflammatory responses to innocuous foreign antigens. Treg cell dysfunction has been linked to many inflammatory diseases, including allergic airway inflammation. Glucocorticoids that are used to treat allergic airway inflammation and asthma are thought to work in part by promoting Treg cell differentiation; patients who are refractory to these drugs have defective induction of anti-inflammatory Treg cells. Previous observations suggest that Treg cells deficient in the transcription factor FoxO1 are pro-inflammatory, and that FoxO1 activity is regulated by its phosphorylation status and nuclear localization. Here, we asked whether altering the phosphorylation state of FoxO1 through modulation of a regulatory phosphatase might affect Treg cell function. In a mouse model of house dust mite-induced allergic airway inflammation, we observed robust recruitment of Treg cells to the lungs and lymph nodes of diseased mice, without an apparent increase in the Treg cytokine interleukin-10 in the airways. Intriguingly, expression of PP2A, a serine/threonine phosphatase linked to the regulation of FoxO1 phosphorylation, was decreased in the mediastinal lymph nodes of HDM-treated mice, mirroring the decreased PP2A expression seen in peripheral blood monocytes of glucocorticoid-resistant asthmatic patients. When we asked whether modulation of PP2A activity alters Treg cell function via treatment with the PP2A inhibitor okadaic acid, we observed increased phosphorylation of FoxO1 and decreased nuclear localization. However, dysregulation of FoxO1 did not impair Treg cell differentiation ex vivo or cause Treg cells to adopt a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Moreover, inhibition of PP2A activity did not affect the suppressive function of Treg cells ex vivo. Collectively, these data suggest that modulation of the phosphorylation state of FoxO1 via PP2A inhibition does not modify Treg cell function ex vivo. Our data also highlight the caveat in using ex vivo assays of Treg cell differentiation and function, in that while these assays are useful, they may not fully recapitulate Treg cell phenotypes that are observed in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin attenuates airway inflammation through induction of forkhead box protein 3-positive regulatory T cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Jun;129(6):1656-65.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.050. Epub 2012 May 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22564681
-
Therapeutic administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells reduces airway inflammation without up-regulating Tregs in experimental asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2018 Feb;48(2):205-216. doi: 10.1111/cea.13048. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Clin Exp Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29068567
-
Staphylococcus succinus 14BME20 Prevents Allergic Airway Inflammation by Induction of Regulatory T Cells via Interleukin-10.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 4;10:1269. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01269. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31231389 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell regulatory mechanisms in specific immunotherapy.Chem Immunol Allergy. 2008;94:158-177. doi: 10.1159/000155000. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2008. PMID: 18802346 Review.
-
Context-Dependent Effect of Glucocorticoids on the Proliferation, Differentiation, and Apoptosis of Regulatory T Cells: A Review of the Empirical Evidence and Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 6;20(5):1142. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051142. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30845709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin inhibited LPS-induced cytokine storm by interacting with the AKT1-FoxO1 and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in macrophages.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 8;14(1):20913. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71569-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39245773 Free PMC article.
-
FoxO1 regulates TLR4/MyD88/MD2-NF-κB inflammatory signalling in mucosal barrier injury of inflammatory bowel disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Mar;24(6):3712-3723. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15075. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32057181 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatase 2A as a Therapeutic Target in Pulmonary Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Aug 26;59(9):1552. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091552. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FoxO1 is a critical regulator of M2-like macrophage activation in allergic asthma.Allergy. 2019 Mar;74(3):535-548. doi: 10.1111/all.13626. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 30288751 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

