Reactions of Buckwheat-Hypersensitive Patients during Oral Food Challenge Are Rare, but Often Anaphylactic
- PMID: 28268211
- PMCID: PMC5452282
- DOI: 10.1159/000456008
Reactions of Buckwheat-Hypersensitive Patients during Oral Food Challenge Are Rare, but Often Anaphylactic
Abstract
Background: Buckwheat (BW) is a common cause of life-threatening allergy in Asia. Few have examined oral food challenges (OFCs) using BW. We here describe the OFC outcomes for the diagnosis or confirmation of tolerance acquisition and clarify risk factors for positive OFCs.
Methods: Between July 2005 and March 2014, we retrospectively reviewed data from children who underwent OFCs using 3,072 mg of BW protein at Sagamihara National Hospital. Children were suspected of having BW allergy because of positive results for BW-specific IgE or because they had been previously diagnosed with BW allergy owing to immediate reactions to BW.
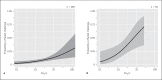
Results: Of 476 such patients, we analyzed 419 aged 1-17 years (median age 6.7 years). Forty-four (10.5%) reacted to the BW OFC and 24 (54.5%) experienced anaphylaxis. Among patients with suspected BW allergies (n = 369), 30 (8.1%) reacted to OFC. However, among patients with definitive BW allergies (n = 50) who underwent OFCs a median of 7.0 years after their last immediate reaction, 14 (28.0%) reacted to OFC. Among 12 patients with past anaphylactic reactions to BW, 8 exhibited tolerance to BW. A history of immediate reaction to BW and high BW-specific IgE levels were significant risk factors for a positive OFC.
Conclusions: BW allergies are rare among children suspected of having BW allergies due to positivity for BW-specific IgE. Most children with definitive BW allergies can tolerate BW, even after anaphylactic reactions. Nevertheless, careful observation is needed when performing BW OFCs, considering the high incidence of anaphylactic reactions.
© 2017 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Specific IgE for Fag e 3 Predicts Oral Buckwheat Food Challenge Test Results and Anaphylaxis: A Pilot Study.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176(1):8-14. doi: 10.1159/000487135. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29635254 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the outcome of the buckwheat oral challenge test: a first evaluation assuming a single serving of boiled buckwheat noodles.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 May;56(3):121-127. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.315. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37712396
-
Skin prick test is more useful than specific IgE for diagnosis of buckwheat allergy: A retrospective cross-sectional study.Allergol Int. 2018 Jan;67(1):67-71. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 May 4. Allergol Int. 2018. PMID: 28479284 Clinical Trial.
-
Buckwheat Allergy in Asia.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Sep;24(9):549-557. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01166-6. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38976201 Review.
-
The impact of oral food challenges for food allergy on quality of life: A systematic review.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018 Aug;29(5):527-537. doi: 10.1111/pai.12905. Epub 2018 May 16. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29660855
Cited by
-
Understanding buckwheat allergies for the management of allergic reactions in humans and animals.Breed Sci. 2020 Mar;70(1):85-92. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.19051. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Breed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32351307 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitizations to wheat and strawberry: are they a tangible threat to atopic Egyptian.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;11(6):84-91. eCollection 2022. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36660140 Free PMC article.
-
IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy in Brazilian children: Outcomes of oral food challenge.World Allergy Organ J. 2023 May 20;16(5):100781. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2023.100781. eCollection 2023 May. World Allergy Organ J. 2023. PMID: 37251812 Free PMC article.
-
Specific IgE for Fag e 3 Predicts Oral Buckwheat Food Challenge Test Results and Anaphylaxis: A Pilot Study.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176(1):8-14. doi: 10.1159/000487135. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29635254 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation in Food Challenge Tests for Food Allergy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Oct 30;18(12):74. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0825-3. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018. PMID: 30377836 Review.
References
-
- Wieslander G. Review on buckwheat allergy. Allergy. 1996;51:661–665. - PubMed
-
- Heffler E, Nebiolo F, Asero R, Guida G, Badiu I, Pizzimenti S, Marchese C, Amato S, Mistrello G, Canaletti F, Rolla G. Clinical manifestations, co-sensitizations, and immunoblotting profiles of buckwheat-allergic patients. Allergy. 2011;66:264–270. - PubMed
-
- Heffler E, Guida G, Badiu I, Nebiolo F, Rolla G. Anaphylaxis after eating Italian pizza containing buckwheat as the hidden food allergen. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2007;17:261–263. - PubMed
-
- Urisu A, Ebisawa M, Ito K, Aihara Y, Ito S, Mayumi M, Kohno Y, Kondo N. Japanese guideline for food allergy 2014. Allergol Int. 2014;63:399–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

