Suppressor analysis of eepR mutant defects reveals coordinate regulation of secondary metabolites and serralysin biosynthesis by EepR and HexS
- PMID: 28270264
- PMCID: PMC5775897
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.000422
Suppressor analysis of eepR mutant defects reveals coordinate regulation of secondary metabolites and serralysin biosynthesis by EepR and HexS
Abstract
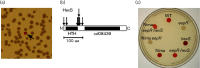
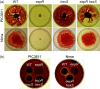
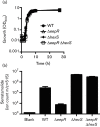
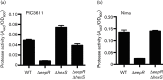
The EepR transcription factor positively regulates secondary metabolites and tissue-damaging metalloproteases. To gain insight into mechanisms by which EepR regulates pigment and co-regulated factors, genetic suppressor analysis was performed. Suppressor mutations that restored pigment to the non-pigmented ∆eepR mutant mapped to the hexS ORF. Mutation of hexS also restored haemolysis, swarming motility and protease production to the eepR mutant. HexS is a known direct and negative regulator of secondary metabolites in Serratia marcescens and is a LysR family regulator and an orthologue of LrhA. Here, we demonstrate that HexS directly controls eepR and the serralysin gene prtS. EepR was shown to directly regulate eepR expression but indirectly regulate hexS expression. Together, these data indicate that EepR and HexS oppose each other in controlling stationary phase-associated molecules and enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Williamson NR, Simonsen HT, Harris AK, Leeper FJ, Salmond GP. Disruption of the copper efflux pump (CopA) of Serratia marcescens ATCC 274 pleiotropically affects copper sensitivity and production of the tripyrrole secondary metabolite, prodigiosin. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;33:151–158. doi: 10.1007/s10295-005-0040-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

