All mixed up: defining roles for β-cell subtypes in mature islets
- PMID: 28270515
- PMCID: PMC5358720
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.294389.116
All mixed up: defining roles for β-cell subtypes in mature islets
Abstract
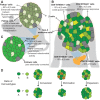
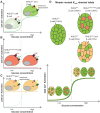
Following differentiation during fetal development, β cells further adapt to their postnatal role through functional maturation. While adult islets are thought to contain functionally mature β cells, recent analyses of transgenic rodent and human pancreata reveal a number of novel heterogeneity markers in mammalian β cells. The marked heterogeneity long after maturation raises the prospect that diverse populations harbor distinct roles aside from glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In this review, we outline our current understanding of the β-cell maturation process, emphasize recent literature on novel heterogeneity markers, and offer perspectives on reconciling the findings from these two areas.
Keywords: aging; maturation; pancreatic islets; stem cell differentiation; β-cell; β-cell heterogeneity.
© 2017 Liu and Hebrok; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Zavacki AM, Marinelarena A, Hollister-Lock J, El Khattabi I, Marsili A, Weir GC, Sharma A, Larsen PR, Bonner-Weir S. 2013. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic β-cell development and glucose-responsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes 62: 1569–1580. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
