Viewing oxidative stress through the lens of oxidative signalling rather than damage
- PMID: 28270560
- PMCID: PMC5469280
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160814
Viewing oxidative stress through the lens of oxidative signalling rather than damage
Abstract
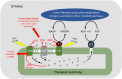
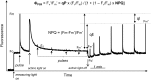
Concepts of the roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plants and animals have shifted in recent years from focusing on oxidative damage effects to the current view of ROS as universal signalling metabolites. Rather than having two opposing activities, i.e. damage and signalling, the emerging concept is that all types of oxidative modification/damage are involved in signalling, not least in the induction of repair processes. Examining the multifaceted roles of ROS as crucial cellular signals, we highlight as an example the loss of photosystem II function called photoinhibition, where photoprotection has classically been conflated with oxidative damage.
Keywords: cell signalling; oxidative stress; photoinhibition; photosynthesis; reactive oxygen species.
© 2017 The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society and distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution Licence 4.0 (CC BY).
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson L.E. and Duggan J.X. (1976) Light modulation of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Partial characterisation of the light inactivation system and its effects on the properties of the chloroplastic and cytoplasmic forms of the enzyme. Plant Physiol. 58, 135–139 doi:10.1104/pp.58.2.135 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahlfors R., Macioszek V., Rudd J., Brosché M., Schlichting R., Scheel D. et al. (2004) Stress hormone-independent activation and nuclear translocation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis thaliana during ozone exposure. Plant J. 40, 512–522 doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02229.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

