Regulation of MUC5B Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 28272906
- PMCID: PMC5516283
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0046OC
Regulation of MUC5B Expression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
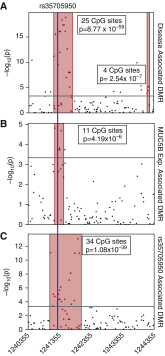
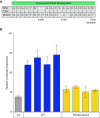
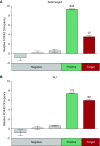
The gain-of-function mucin 5B (MUC5B) promoter variant, rs35705950, confers the largest risk, genetic or otherwise, for the development of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; however, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of MUC5B expression have yet to be elucidated. Here, we identify a critical regulatory domain that contains the MUC5B promoter variant and has a highly conserved forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2) binding motif. This region is differentially methylated in association with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, MUC5B expression, and rs35705950. In addition, we show that this locus binds FOXA2 dynamically, and that binding of FOXA2 is necessary for enhanced expression of MUC5B. In aggregate, our findings identify novel targets to regulate the expression of MUC5B.
Keywords: DNA methylation; gene regulation; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; mucin 5B; mucins.
Figures



References
-
- Korfei M, Schmitt S, Ruppert C, Henneke I, Markart P, Loeh B, Mahavadi P, Wygrecka M, Klepetko W, Fink L, et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of lung tissue from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and lung transplant donor lungs. J Proteome Res. 2011;10:2185–2205. - PubMed
-
- Korfei M, Skwarna S, Henneke I, MacKenzie B, Klymenko O, Saito S, Ruppert C, von der Beck D, Mahavadi P, Klepetko W, et al. Aberrant expression and activity of histone deacetylases in sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax. 2015;70:1022–1032. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

