Reversal of DDK-Mediated MCM Phosphorylation by Rif1-PP1 Regulates Replication Initiation and Replisome Stability Independently of ATR/Chk1
- PMID: 28273463
- PMCID: PMC5357733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.042
Reversal of DDK-Mediated MCM Phosphorylation by Rif1-PP1 Regulates Replication Initiation and Replisome Stability Independently of ATR/Chk1
Abstract
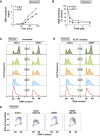
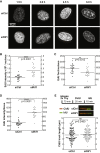
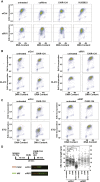
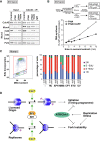
Dbf4-dependent kinases (DDKs) are required for the initiation of DNA replication, their essential targets being the MCM2-7 proteins. We show that, in Xenopus laevis egg extracts and human cells, hyper-phosphorylation of DNA-bound Mcm4, but not phosphorylation of Mcm2, correlates with DNA replication. These phosphorylations are differentially affected by the DDK inhibitors PHA-767491 and XL413. We show that DDK-dependent MCM phosphorylation is reversed by protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) targeted to chromatin by Rif1. Loss of Rif1 increased MCM phosphorylation and the rate of replication initiation and also compromised the ability of cells to block initiation when challenged with replication inhibitors. We also provide evidence that Rif1 can mediate MCM dephosphorylation at replication forks and that the stability of dephosphorylated replisomes strongly depends on Chk1 activity. We propose that both replication initiation and replisome stability depend on MCM phosphorylation, which is maintained by a balance of DDK-dependent phosphorylation and Rif1-mediated dephosphorylation.
Keywords: Cdc7; DNA damage; DNA replication; MCM; Rif1; Xenopus egg cell-free system; checkpoint signaling; human tissue culture.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Costanzo V., Shechter D., Lupardus P.J., Cimprich K.A., Gottesman M., Gautier J. An ATR- and Cdc7-dependent DNA damage checkpoint that inhibits initiation of DNA replication. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:203–213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

