Effects of hydrotalcite combined with esomeprazole on gastric ulcer healing quality: A clinical observation study
- PMID: 28275307
- PMCID: PMC5323452
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1268
Effects of hydrotalcite combined with esomeprazole on gastric ulcer healing quality: A clinical observation study
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effects of hydrotalcite combined with esomeprazole on gastric ulcer healing quality.
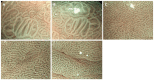
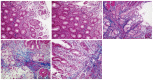
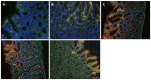
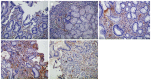
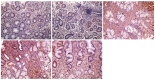
Methods: Forty-eight patients diagnosed with gastric ulcer between June 2014 and February 2016 were randomly allocated to the combination therapy group or monotherapy group. The former received hydrotalcite combined with esomeprazole, and the latter received esomeprazole alone, for 8 wk. Twenty-four healthy volunteers were recruited and acted as the healthy control group. Endoscopic ulcer healing was observed using white light endoscopy and narrow band imaging magnifying endoscopy. The composition of collagen fibers, amount of collagen deposition, expression of factor VIII and TGF-β1, and hydroxyproline content were analyzed by Masson staining, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescent imaging and ELISA.
Results: Following treatment, changes in the gastric microvascular network were statistically different between the combination therapy group and the monotherapy group (P < 0.05). There were significant differences (P < 0.05) in collagen deposition, expression level of Factor VIII and TGF-β1, and hydroxyproline content in the two treatment groups compared with the healthy control group. These parameters in the combination therapy group were significantly higher than in the monotherapy group (P < 0.05). The ratio of collagen I to collagen III was statistically different among the three groups, and was significantly higher in the combination therapy group than in the monotherapy group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Hydrotalcite combined with esomeprazole is superior to esomeprazole alone in improving gastric ulcer healing quality in terms of improving microvascular morphology, degree of structure maturity and function of regenerated mucosa.
Keywords: Esomeprazole; Gastric ulcer; Hydrotalcite; Quality of ulcer healing.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures

References
-
- Tarnawski A, Stachura J, Krause WJ, Douglass TG, Gergely H. Quality of gastric ulcer healing: a new, emerging concept. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1991;13 Suppl 1:S42–S47. - PubMed
-
- Fornai M, Colucci R, Antonioli L, Awwad O, Ugolini C, Tuccori M, Fulceri F, Natale G, Basolo F, Blandizzi C. Effects of esomeprazole on healing of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced gastric ulcers in the presence of a continued NSAID treatment: Characterization of molecular mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 2011;63:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Tarnawski A, Ahluwalia A, Jones MK. Gastric cytoprotection beyond prostaglandins: cellular and molecular mechanisms of gastroprotective and ulcer healing actions of antacids. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:126–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

