Characterization of Human AB Serum for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Expansion
- PMID: 28275329
- PMCID: PMC5318935
- DOI: 10.1159/000448196
Characterization of Human AB Serum for Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Expansion
Abstract
Background: So far, using human blood-derived components appears to be the most efficient and safest approach available for mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) expansion. In this paper, we report on the characterization of human AB serum (AB HS) produced by using different plasma sources, and its use as an alternative supplement to MSC expansion.
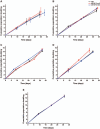
Methods: Two plasma sources were used for AB HS production: plasma removed from whole blood after 24 h of collection (PC > 24 h) and plasma, cryoprecipitate reduced (PCryoR). The biochemical profile and quality of the produced AB HS batches were analyzed and their ability to support MSC cell growth after different storage times (0, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months) was evaluated.
Results: The two plasma sources used showed similar characteristics regarding biochemical constituents and quality parameters and were effective in promoting MSC growth. MSCs cultured in medium supplemented with 10% AB HS presented similar doubling times and cumulative population doublings when compared to the 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS)-supplemented culture while maintaining immunophenotype, functional features, and cytogenetic profile.
Conclusion: Overall, the results indicate that AB HS is an efficient FBS substitute and can be used for at least 12 months after production without impairing cell proliferation and quality.
Keywords: Cell expansion; Fetal bovine serum; Human AB serum; Mesenchymal stromal cells.
Figures


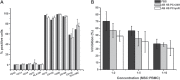


Similar articles
-
Human alternatives to fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow.Stem Cells. 2009 Sep;27(9):2331-41. doi: 10.1002/stem.139. Stem Cells. 2009. PMID: 19544413
-
The Biological Characteristics of Placenta Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cultured in Human Serum.J Med Assoc Thai. 2016 Jul;99 Suppl 4:S75-83. J Med Assoc Thai. 2016. PMID: 29917345
-
Human serum enhances the proliferative capacity and immunomodulatory property of MSCs derived from human placenta and umbilical cord.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Mar 7;10(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1175-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30845980 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet lysate as a substitute for animal serum for the ex-vivo expansion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: present and future.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 Jul 13;7(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0352-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27411942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scalable microcarrier-based manufacturing of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.J Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 20;236:88-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27527397 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of a simple and efficient platform for car-t cell generation and expansion: from lentiviral production to in vivo studies.Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2020 Apr-Jun;42(2):150-158. doi: 10.1016/j.htct.2019.06.007. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther. 2020. PMID: 31676276 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: From Discovery to Manufacturing and Commercialization.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Apr 11;2018:4083921. doi: 10.1155/2018/4083921. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 30057622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel xeno-free culture system for human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Int J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr 18;12(4):563-570. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2019.04.06. eCollection 2019. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31024807 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing the biomolecular relevance of cell culture practice.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Jan 3;32(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01095-6. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 39748368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Fully-Closed and Automated Hollow Fiber Bioreactor for Clinical-Grade Manufacturing of Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018 Feb;14(1):141-143. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9787-4. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018. PMID: 29188439 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dimarakis I, Levicar N. Cell culture medium composition and translational adult bone marrow-derived stem cell research. Stem Cells. 2006;24:1407–1408. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

