Factors associated with time to achieve an undetectable HIV RNA viral load after start of antiretroviral treatment in HIV-1-infected pregnant women
- PMID: 28275456
- PMCID: PMC5337419
- DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30294-6
Factors associated with time to achieve an undetectable HIV RNA viral load after start of antiretroviral treatment in HIV-1-infected pregnant women
Abstract
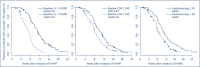
Objective: To identify factors associated with the time to viral suppression in women starting antiretroviral treatment (ART) during pregnancy. Knowledge on duration of viral load (VL) decline could help deciding the timing of treatment initiation.
Methods: Highly active antiretroviral treatment (HAART)-naive pregnant women over 18 years of age who started treatment during pregnancy were included. The time to viral suppression was calculated and compared between subgroups.
Results: A total of 227 pregnancies matched our inclusion criteria. In 84.6% of these an undetectable VL was reached at the time of delivery. The median time to undetectable VL after initiation of treatment was 60 days (12-168 days). Only baseline VL <10,000 copies/mL showed an independent association with time to viral suppression in multivariate Cox regression analysis, with a mean time to reach a VL <50 HIV-1 copies/mL of 49 days (95% CI 44-53). No difference in time to undetectable VL was found between protease inhibitor and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-based regimens. Integrase inhibitors were not part of any treatment regimen.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that in patients with baseline HIV RNA <10,000 copies/mL ART initiation might be postponed up to the twentieth week of pregnancy, thus minimising the risk of possible drug-related teratogenicity and toxicity.
Keywords: HIV; pregnancy; suppression; undetectable.
Figures
References
-
- European Collaborative S Mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 458– 465. - PubMed
-
- Tubiana R, Le Chenadec J, Rouzioux C et al. . Factors associated with mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 despite a maternal viral load <500 copies/ml at delivery: a case-control study nested in the French perinatal cohort (EPF-ANRS CO1). Clin Infect Dis 2010; 50: 585– 596. - PubMed
-
- Stichting HIV Monitoring Monitoring report 2014: human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in the Netherlands. Available at: www.hiv-monitoring.nl/english/research/monitoringreports/ ( accessed December 2016).
-
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor HIV Behandelaren HIV richtlijn: hoofdstuk 7. 2015.
-
- Panel on Treatment of HIV Infected Pregnant Women and Prevention of Perinatal Transmission Recommendations for use of antiretroviral drugs in pregnant HIV-1-infected women for maternal health and interventions to reduce perinatal HIV transmission in the United States. Section Antepartum care. Rockville (MD): Public Health Service Task Force, 2016. ( Last updated: April 29, 2016). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources