Molecular Targeted Agents for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Status and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 28275577
- PMCID: PMC5340214
- DOI: 10.1159/000452138
Molecular Targeted Agents for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Status and Future Perspectives
Figures

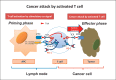
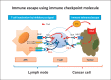
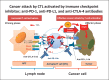

References
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Häussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J, SHARP Investigators Study Group Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Takayama T, Mazzaferro V, Chau GY, Yang J, Kudo M, Cai J, Poon RT, Han KH, Tak WY, Lee HC, Song T, Roayaie S, Bolondi L, Lee KS, Makuuchi M, Souza F, Berre MA, Meinhardt G, Llovet JM, STORM Investigators Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1344–1354. - PubMed
-
- Okita K, Izumi N, Matsui O, Tanaka K, Kaneko S, Moriwaki H, Ikeda K, Osaki Y, Numata K, Nakachi K, Kokudo N, Imanaka K, Nishiguchi S, Okusaka T, Nishigaki Y, Shiomi S, Kudo M, Ido K, Karino Y, Hayashi N, Ohashi Y, Makuuchi M, Kumada H, Peretinoin Study Group Peretinoin after curative therapy of hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:191–202. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Imanaka K, Chida N, Nakachi K, Tak WY, Takayama T, Yoon JH, Hori T, Kumada H, Hayashi N, Kaneko S, Tsubouchi H, Suh DJ, Furuse J, Okusaka T, Tanaka K, Matsui O, Wada M, Yamaguchi I, Ohya T, Meinhardt G, Okita K. Phase III study of sorafenib after transarterial chemoembolisation in Japanese and Korean patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:2117–2127. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

