The human mitochondrial transcription factor A is a versatile G-quadruplex binding protein
- PMID: 28276514
- PMCID: PMC5343656
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43992
The human mitochondrial transcription factor A is a versatile G-quadruplex binding protein
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The human mitochondrial transcription factor A is a versatile G-quadruplex binding protein.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 6;7:45948. doi: 10.1038/srep45948. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28383057 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
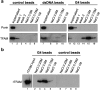
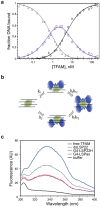
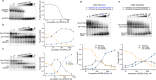
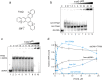
The ability of the guanine-rich strand of the human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) to form G-quadruplex structures (G4s) has been recently highlighted, suggesting potential functions in mtDNA replication initiation and mtDNA stability. G4 structures in mtDNA raise the question of their recognition by factors associated with the mitochondrial nucleoid. The mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), a high-mobility group (HMG)-box protein, is the major binding protein of human mtDNA and plays a critical role in its expression and maintenance. HMG-box proteins are pleiotropic sensors of DNA structural alterations. Thus, we investigated and uncovered a surprising ability of TFAM to bind to DNA or RNA G4 with great versatility, showing an affinity similar than to double-stranded DNA. The recognition of G4s by endogenous TFAM was detected in mitochondrial extracts by pull-down experiments using a G4-DNA from the mtDNA conserved sequence block II (CSBII). Biochemical characterization shows that TFAM binding to G4 depends on both the G-quartets core and flanking single-stranded overhangs. Additionally, it shows a structure-specific binding mode that differs from B-DNA, including G4-dependent TFAM multimerization. These TFAM-G4 interactions suggest functional recognition of G4s in the mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Architectural role of mitochondrial transcription factor A in maintenance of human mitochondrial DNA.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):9823-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.9823-9834.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509786 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulates mitochondrial transcription initiation, DNA packaging, and genome copy number.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep-Oct;1819(9-10):921-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.03.002. Epub 2012 Mar 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22465614 Review.
-
Mitochondrial nucleoid and transcription factor A.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Apr;1011:61-8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-41088-2_7. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15126284
-
Interaction of human mitochondrial transcription factor A in mitochondria: its involvement in the dynamics of mitochondrial DNA nucleoids.Genes Cells. 2015 Dec;20(12):1017-27. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12306. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Genes Cells. 2015. PMID: 26445116
-
Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through TFAM-mitochondrial DNA interactions: Useful insights from aging and calorie restriction studies.Mitochondrion. 2015 Nov;25:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 3. Mitochondrion. 2015. PMID: 26437364 Review.
Cited by
-
Possible frequent multiple mitochondrial DNA copies in a single nucleoid in HeLa cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 8;13(1):5788. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33012-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37031254 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA-Binding High-Mobility Group Box Domain of Sox Family Proteins Directly Interacts with RNA In Vitro.Biochemistry. 2022 May 5:10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00218. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00218. Online ahead of print. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35511045 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of proteostasis and innate immunity via mitochondria-nuclear communication.J Cell Biol. 2024 Mar 4;223(3):e202310005. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202310005. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38335010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The DNA binding high mobility group box protein family functionally binds RNA.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Sep-Oct;14(5):e1778. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1778. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 36646476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural analysis of the Candida albicans mitochondrial DNA maintenance factor Gcf1p reveals a dynamic DNA-bridging mechanism.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 23;51(11):5864-5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad397. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37207342 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

