Adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy on liver hepatocytes and endothelium in HIV patients: An ultrastructural perspective
- PMID: 28277148
- PMCID: PMC6077994
- DOI: 10.1080/01913123.2017.1282066
Adverse effects of antiretroviral therapy on liver hepatocytes and endothelium in HIV patients: An ultrastructural perspective
Abstract
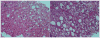
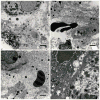
Human immunodeficiency virus and antiretroviral therapy (ART) together can be far more detrimental to liver cells than either of the two unaided. However, ultrastructural aspects of the synergistic effects of HIV and ART have been understudied. In a patient cohort receiving ART, this study characterizes ultrastructurally sinusoidal degeneration, hepatocytic aberrations, mitochondrial dysfunction, accumulation of bulky lipid droplets (steatosis), and occlusion of sinusoidal lumina. Mitochondrial dysfunction causes the accumulation of acetyl-CoA which leads to insulin upregulation and resistance, lipid synthesis, and steatosis. Lipid droplets deposited in the sinusoids could be the source of the blood's lipid profile alterations in HIV patients on ART.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; HIV; endothelium; hepatotoxicity; liver; mitochondria; sinusoid; steatosis.
Figures
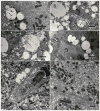
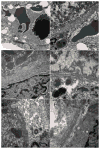
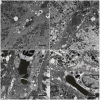
References
-
- Prevention CfDCa. Diagnoses of HIV Infection in the United States and Dependent Areas, 2014. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2015. p. 26.
-
- Joshi D, O’Grady J, Dieterich D, Gazzard B, Agarwal K. Increasing burden of liver disease in patients with HIV infection. Lancet. 2011;377(9772):1198–1209. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
