The demanding attention of tuberculosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: High incidence compared with general population
- PMID: 28278166
- PMCID: PMC5344370
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173250
The demanding attention of tuberculosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: High incidence compared with general population
Abstract
Background: The risk of developing tuberculosis (TB) in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) recipients is expected to be relatively high in an intermediate TB burden country. This single-center retrospective study was conducted to investigate risk factors and the incidence of TB after allogeneic HSCT.
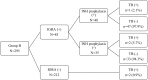
Methods: From January 2004 to March 2011, 845 adult patients were enrolled. Starting April 2009, patients were given isoniazid (INH) prophylaxis based on interferon-γ release assay results. The incidence of TB was analyzed before and after April 2009, and compared it with that of the general population in Korea.
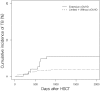
Results: TB was diagnosed in 21 (2.49%) of the 845 allogeneic HSCT patients. The median time to the development of TB was 386 days after transplantation (range, 49-886). Compared with the general population, the standardized incidence ratio of TB was 9.10 (95% CI; 5.59-14.79). Extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was associated with the development of TB (P = 0.003). Acute GVHD, conditioning regimen with total body irradiation and conditioning intensity were not significantly related. INH prophylaxis did not reduce the incidence of TB (P = 0.548). Among 21 TB patients, one patient had INH prophylaxis.
Conclusion: Allogeneic HSCT recipients especially those who suffer from extensive chronic GVHD are at a high risk of developing TB. INH prophylaxis did not statistically change the incidence of TB, however, further well-designed prospective studies are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence and clinical profile of tuberculosis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.Transpl Infect Dis. 2018 Feb;20(1). doi: 10.1111/tid.12794. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Transpl Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29064140
-
The incidence of tuberculosis infection in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients: A retrospective cohort study from a center in Turkey.Transpl Infect Dis. 2018 Aug;20(4):e12912. doi: 10.1111/tid.12912. Epub 2018 May 9. Transpl Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29679523
-
Long-term risk of tuberculosis in haematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: a 10-year nationwide study.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015 Jan;19(1):58-64. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.14.0301. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015. PMID: 25519791
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Tuberculosis in blood and marrow transplant recipients.Hematol Oncol. 2002 Jun;20(2):51-62. doi: 10.1002/hon.681. Hematol Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12111868 Review.
Cited by
-
Infectious complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: current status and future perspectives in Korea.Korean J Intern Med. 2018 Mar;33(2):256-276. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2018.036. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Korean J Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29506345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disseminated Tuberculosis with Cholecystitis in a Patient after Cord Blood Transplantation.Intern Med. 2020 Nov 1;59(21):2769-2771. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4923-20. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32669496 Free PMC article.
-
Study of clinical characteristics, risk factors and outcomes for tuberculosis post allogeneic stem cell transplant: never count it out.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2021 Apr 12;8:20499361211008674. doi: 10.1177/20499361211008674. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33912346 Free PMC article.
-
Latent Tuberculosis Infection in Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: A Retrospective Italian Cohort Study in Tor Vergata University Hospital, Rome.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 27;19(17):10693. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710693. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36078409 Free PMC article.
-
High Tuberculosis Density Incidence Rate in Matched Unrelated Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients in the State of São Paulo, Brazil.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 1;15(1):e2023037. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2023.037. eCollection 2023. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37435037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arslan O, Gurman G, Dilek I, Ozcan M, Koc H, Ilhan O, et al. Incidence of tuberculosis after bone marrow transplantation in a single center from Turkey. Haematologia (Budap). 1998;29: 59–62 - PubMed
-
- Ku SC, Tang JL, Hsueh PR, Luh KT, Yu CJ, Yang PC. Pulmonary tuberculosis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001;27: 1293–1297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

